Dear AuntMinnie Member,
In a surprising new study released today, Japanese researchers have discovered that there may be a relationship between MRI contrast and brain abnormalities -- a finding that once again raises questions about the safety of gadolinium-based contrast.
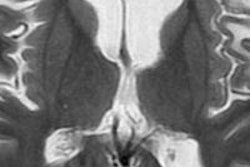
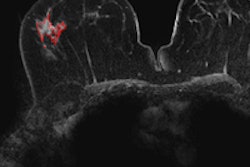
In a small patient population, the group found that individuals who received more contrast-enhanced MRI scans had stronger hyperintensities in two areas of the brain than patients who received fewer scans. In addition, the strength of the hyperintensity correlated with the number of administrations of gadolinium contrast.
The researchers speculated that the hyperintensities were present because gadolinium -- a toxic compound -- remained in the body even in patients with normal renal function. Read more about this intriguing new study by clicking here.
fMRI detects resident burnout
In other MRI-related news, U.S. researchers using functional MRI (fMRI) made some interesting discoveries regarding the level of burnout in resident physicians.
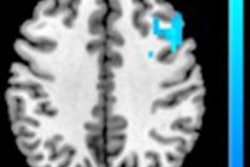
The researchers used fMRI to scan both residents and faculty physicians while they pondered clinical questions. The results of the scans were then compared with each subject's level of burnout as derived from a questionnaire given before the scans were acquired.
Interestingly, the resident subjects had altered fMRI signals that correlated with their higher reported levels of depersonalization and emotional exhaustion, while the attending physicians showed no link between fMRI signal and reported burnout levels.
What are the reasons behind the discrepancy? You'll have to click here to find out, or visit our MRI Digital Community at mri.auntminnie.com.