By attaching compounds extracted from green tea to contrast nanoparticles, researchers from Germany say they have enhanced MRI scans of malignant tumors in mice.
The study by lead author Lisong Xiao, from the University of Cologne, and colleagues was published online March 2 in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. The article details how they used a one-step process to coat iron-oxide nanoparticles with green tea compounds called catechins and administered them to mice with cancer. The objective was to see if the green tea compounds, which are thought to have anticancer and anti-inflammatory properties, could aid MRI results.
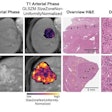
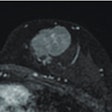
The MR images showed the novel imaging agent gathering in tumor cells, thus providing a strong contrast from surrounding nontumor cells. The catechin-coated nanoparticles are promising candidates for use in MRI and related applications, the researchers concluded.

.fFmgij6Hin.png?auto=compress%2Cformat&fit=crop&h=100&q=70&w=100)

.fFmgij6Hin.png?auto=compress%2Cformat&fit=crop&h=167&q=70&w=250)