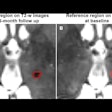
Researchers from Canada have developed a machine-learning algorithm capable of identifying schizophrenia on functional MRI (fMRI) scans of the brain, according to a study recently published online in Molecular Psychiatry.
Determining the ideal treatment strategy for a patient with schizophrenia is a challenging task that often involves trial and error, noted first author Bo Cao, PhD, from the University of Alberta.
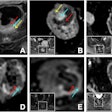
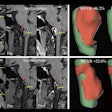
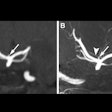
To improve this process, Cao and colleagues used their machine-learning algorithm to examine brain fMRI scans of individuals with or without schizophrenia. By assessing the functional connections between the superior temporal cortex and other regions of the brain, the algorithm was able to identify schizophrenia with 78.6% accuracy. It also predicted whether a patient would respond to the antipsychotic drug risperidone with 82.5% accuracy (Mol Psychiatry, June 19, 2018).
"This is the first step, but ultimately we hope to find reliable biomarkers that can predict schizophrenia before the symptoms show up," Cao said in a statement from the university. "In the future, with the help of machine learning, if the doctor can select the best medicine or procedure for a specific patient at the first visit, it would be a good step forward."