Wednesday, November 28 | 11:40 a.m.-11:50 a.m. | SSK03-08 | Room S102CD
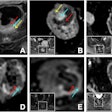
In this session, Japanese researchers will share results from their newly developed deep-learning reconstruction technique designed to improve image quality for noncontrast coronary MR angiography.The study, scheduled for presentation by Dr. Daisuke Utsunomiya from Kumamoto University, included 10 volunteers with no evidence of coronary artery disease. Noncontrast coronary MR angiography scans were performed on a 3-tesla MRI scanner (Galan 3T XGO, Canon Medical Systems), from which the researchers measured the signal-to-noise ratio of three coronary vessels (proximal and distal segments).
In addition, a dedicated workstation was used to generate moderate and high-level images using the deep-learning reconstruction technique. Two observers graded the vessel visualization and artifacts on a four-point scale, with 1 as the worst and 4 as the best.
Upon further review, visual scores for overall image quality and image noise were significantly better with deep-learning reconstruction than with the original coronary MR angiography. The deep-learning reconstruction technique also provided a higher contrast-to-noise ratio with no degradation in vessel sharpness.
With the advantage of sharper images and improved visualization of coronary arteries, clinicians can noninvasively evaluate the heart more efficiently, Utsunomiya and colleagues noted.