CHICAGO - Ultrasound-guided hydrodissection is an effective treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome, according to research results presented November 30 at RSNA meeting.
A team led by Dr. Anupama Tandon of the University College of Medical Sciences in Delhi, India, and colleagues found that at six-month follow-up, hydrodissection delivered complete and long-term relief to patients.
"It came as a pleasant surprise when this simple procedure of ultrasound-guided hydrodissection provided patients with long-term relief," Tandon said in an RSNA statement.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is the most common and widely known form of entrapment neuropathy, affecting about 3% of the U.S. population. Steroid injections and surgery are often required to treat the condition, with most common surgical method involving cutting the carpal ligament to reduce pressure on the median nerve.
Hydrodissection is a less invasive alternative, involving the injection of a liquid -- usually saline -- into the nerve to separate it from the surrounding tissue. Ultrasound is used during the procedure to accurately identify nerves.
Tandon and colleagues sought to assess the efficacy of hydrodissection for carpal tunnel syndrome treatment via a study that included 63 patients. Participants were divided into three groups: One which received ultrasound-guided hydrodissection with just a saline injection; a second which received ultrasound-guided hydrodissection with an injection mixture of saline and corticosteroid; and a third which received just an ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection with no hydrodissection. The team followed up with patients at four weeks, 12 weeks, and six months post-procedure.
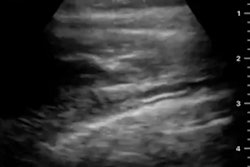
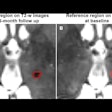
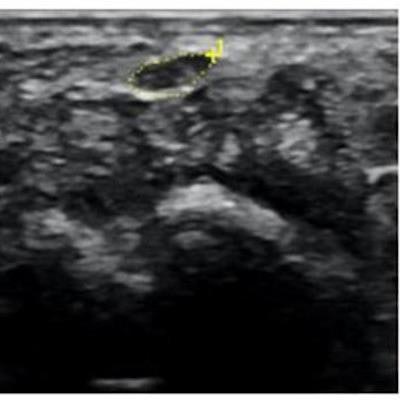
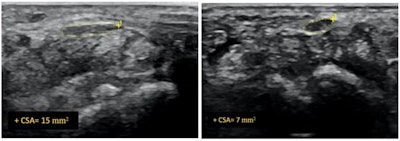 Ultrasound image of median nerve before and after hydrodissection procedure in a patient with carpal tunnel syndrome. This case had cross-sectional area of 12 mm2 pre procedure that reduced to 7 mm2 post procedure (dashed yellow lines depicting the median nerve). Image courtesy of RSNA and Dr. Anupama Tandon.
Ultrasound image of median nerve before and after hydrodissection procedure in a patient with carpal tunnel syndrome. This case had cross-sectional area of 12 mm2 pre procedure that reduced to 7 mm2 post procedure (dashed yellow lines depicting the median nerve). Image courtesy of RSNA and Dr. Anupama Tandon.All three groups of patients showed a reduction in pain at the four-week mark. By the 12-week and six-month mark, both groups that received ultrasound-guided hydrodissection showed further improvement, while the group that received just a corticosteroid injection reported a recurrence of symptoms. In addition, follow-up ultrasounds showed a significant reduction of median nerve cross-sectional area in both hydrodissection groups, with group one demonstrating a reduction of 43% and group two of 46%. Group three showed only an 11% reduction.
"The procedure is short, requiring only 10 to 15 minutes, and is cost-effective, since it doesn't require any high-end equipment," Tandon concluded.