Abnormal interpretation rates for digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and whole-breast ultrasound (WBUS) vary with age among women, according to research presented December 4 at RSNA 2025.
In her talk, Liane Philpotts, MD, from Yale University in New Haven, CT, reported her team’s findings. For women younger than 65, the abnormal interpretation rate is lower with combined DBT and WBUS than with DBT alone. But this rate is similar between the two groups for women ages 65 and older.
“Same-day WBUS permits detection of clinically important cancers not detected on DBT while not significantly changing or even improving abnormal interpretation rates,” Philpotts said.
Breast density and cancer rates vary with age, with older women typically having less density than younger women. However, breast cancer risk increases with age. Screening ultrasound is one supplemental imaging method for women with dense breasts.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2023 enacted a mandate requiring health facilities to disclose breast density status to women. However, Medicare has denied coverage for supplemental screening ultrasound in women with dense breasts.
Philpotts and colleagues studied trends in abnormal interpretation rates and supplemental cancer detection from WBUS in conjunction with DBT. They compared these findings with those of women not undergoing WBUS as a function of age.
The study included 93,189 DBT screenings performed over a three-year period. Of the screenings, 60,152 were performed in women younger than 65, and 33,037 took place among women ages 65 and older. All exams were batch-read offline by 12 dedicated breast radiologists.
Of the screenings in the younger group, 23,672 were dense (39%), and 14,702 (62%) underwent same-day DBT plus WBUS. And for the older group, 8,444 screenings were dense (26%), and 5,837 (69%) underwent same-day DBT plus WBUS.
While the younger cohort had a higher abnormal interpretation rate for DBT alone, this rate was similar between DBT alone and DBT plus WBUS in the older cohort.
Abnormal interpretation rates among younger, older women undergoing DBT, DBT plus WBUS | |||
Cohort | DBT alone | DBT plus WBUS | p-value |
< 65 years | 16.6% | 12.5% | < 0.0001 |
65 years and older | 8.1% | 9.1% | 0.13 |
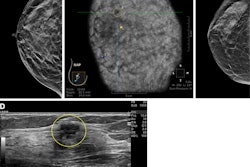
Philpotts also reported that 24 additional cancers were detected by WBUS for a supplemental cancer detection rate of 1.1 per 1,000 screenings. These included 23 invasive cancers and one case of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
Twelve of these cancers were in the younger cohort (cancer detection rate, 0.8/1,000) and the other 12 were in the older cohort (cancer detection rate, 2/1,000). This made for a significantly higher positive predictive value in women ages 65 and older (p = 0.024).
Philpotts concluded that, while combined DBT and WBUS in older women with dense breasts has a similar abnormal interpretation rate to DBT alone, it has a high positive predictive value for supplemental cancers found.