Monday, November 26 | 11:10 a.m.-11:20 a.m. | RC215-13 | Arie Crown Theater
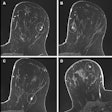
Mammography computer-aided detection (CAD) software based on deep learning can perform comparably to radiologists in detecting breast cancer and at a higher level than traditional mammography CAD applications, according to Dutch researchers.Breast cancer screening programs are considered effective for lowering breast cancer-related mortality, but there's still room for improvement, according to presenter Ioannis Sechopoulos, PhD, of Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
"The high workload combined with the increasing lack of screening radiologists and a significant percentage of cancers being overlooked or misinterpreted are two crucial points where radiologists could use CAD systems as a support tool," he said.
However, traditional CAD software -- despite widespread use -- has never been shown to improve screening, mainly due to high false-positive rates, Sechopoulos noted. Given the recent advances in deep-learning algorithms, the researchers wanted to assess how the standalone performance of a commercial deep learning-based CAD software application -- Transpara (ScreenPoint Medical) -- would compare with radiologists' interpretations.
The study involved nine datasets compiled from seven countries and included a total of 2,458 exams, as well as interpretations from 101 radiologists. The results showed that the software yielded performance that approached the level of an average breast radiologist and was better than traditional CAD software, he said.
"This suggests that [the deep learning-based CAD software has] the potential to make a positive impact in screening programs by being used as a tool to reduce and optimize workload and to improve radiologists' accuracy," Sechopoulos told AuntMinnie.com.
What else did they find? Stop by this Monday morning talk to learn more.