Dutch women's imaging software developer ScreenPoint Medical is touting the results of a new study that found its Transpara artificial intelligence (AI)-based software improved the performance of radiologists in detecting breast cancer.
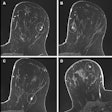
In the study, published online November 20 in Radiology, 14 radiologists interpreted screening mammograms with and without Transpara software and provided a BI-RADS score and probability of malignancy. With the use of Transpara, radiologists had an average area under the curve (AUC) of 0.89, a statistically significant improvement (p = 0.002) compared with an AUC of 0.87 without the software. The use of Transpara also increased sensitivity from 83% to 86%, while specificity rose from 77% to 79%. What's more, Transpara decreased the average reading time per case by 4.5%, according to the company.
The improvement in diagnostic performance was most prevalent in the evaluation of equivocal cancers. Overall, the results suggest that the use of Transpara for decision support might prevent missed cancers and relatively common mammography interpretation errors, ScreenPoint said. Because it offers standalone sensitivity and specificity similar to that of radiologists, Transpara -- when combined with single reading -- might also yield a performance similar to double human reading, according to the vendor.
Transpara is currently approved in Europe for use with digital mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT); regulatory clearance in the U.S. is pending.