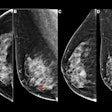
| FIGURE 2.1.5 Long-Standing ulcerative colitis. Contrast-enhanced CT images (A and B) show a striated appearance to the rectosigmoid, with high-attenuation mucosal enhancement and low-attenuation submucosal fat deposition. Prominence of the perirectal fat is also typical. An acute flare of chronic UC is present in this case with superimposed inflammatory stranding. Double-contrast BE images (C and D) from a second patient show uniform luminal narrowing, prominent foreshortening, and loss of the normal haustral appearance, giving the "lead pipe" appearance typical of long-standing UC. Colonoscopy images (E and F) from two separate patients with long-standing disease show loss of the normal mucosal vascular pattern (E) and irregular mucosal scarring from prior inflammation (F). Double-contrast BE image (G) from a different patient shows a foreshortened ahaustral colon with innumerable postinflammatory "filiform" polyps. Colonoscopy images (H and I) from two patients with UC show endoscopic examples of filiform postinflammatory polyps. |
Atlas of Gastrointestinal Imaging Figure 2.1.5 Long-Standing ulcerative colitis
Latest in Home