Dear Advanced Visualization Insider,
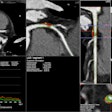
Anomalous aortic origin of the coronary arteries (AAOCA) is a poorly understood congenital abnormality and one of the most common causes of sudden cardiac death in children. 3D printing may be a helpful tool in managing these patients, however.
Researchers have found that 3D-printed models of AAOCA could be accurately produced from CT angiography studies, potentially facilitating risk stratification and treatment decisions. Our coverage of this research is the subject of this edition's Insider Exclusive.
Meanwhile, results from an international study show that a free-breathing, 3D whole-heart T2 MRI mapping sequence can efficiently and reproducibly quantify myocardial T2 times in patients with suspected myocarditis. What's more, the technique can possibly even detect more cases of cardiac inflammation than standard 2D T2 maps.
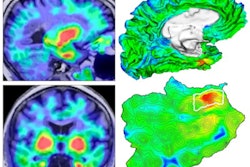
Also, an automated PET image analysis method has revealed an important clue for how Alzheimer's disease could potentially be treated. Researchers found that tau signal emerges initially in the rhinal cortex -- independently of beta-amyloid levels -- before it spreads in the brain. As a result, treatments that target the protein in the rhinal cortex may be able to delay progression of the devastating disease.
PET/CT radiomics and AI show promise for enabling treatment decisions in non-small cell lung cancer without the need for a biopsy. In addition, volumetric analysis of lung consolidation on chest CT scans could be utilized to predict the risk of patients with COVID-19 dying in the hospital.
Furthermore, a method that combines CT radiomics and real-time CT/ultrasound fusion can yield more accurate and efficient tissue biopsies in patients with ovarian cancer. Also, 3D-printed models of wrist fractures based on CT exams acquired at ultralow radiation doses appear to be just as useful as models produced from standard-dose CT images.
The combination of 3D printing and augmented reality technologies can help to deliver better outcomes for planning and guiding thoracoscopic surgeries. Also, prognostic information for survival in lung cancer patients can be quickly obtained by analysis of body composition metrics on abdominal/pelvic CT exams.
MRI radiomics can be an effective aid for predicting axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with early-stage breast cancer. Furthermore, CT radiomics analysis and a machine-learning algorithm can improve preoperative risk classification of complex cystic renal lesions.
3D models that combine vascular and biliary anatomy using different imaging modalities can contribute to more rigorous planning of complex liver operations. In addition, 3D-printed nasopharyngeal swabs have been invaluable in the fight against COVID-19.
Finally, CT radiomics can offer a promising level of accuracy in differentiating noninvasive from invasive pulmonary adenocarcinoma.
Is there a story you'd like to see covered in the Advanced Visualization Community? Please feel free to drop me a line.