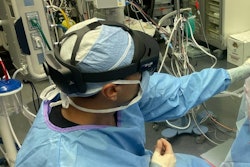
Healthcare IT firm Novarad said that its VisAR augmented-reality (AR) surgical navigation system was used during a successful bilateral sacroiliac joint fusion surgery at EMC Tangerang Hospital in Baten, Indonesia.
VisAR transforms patient imaging data into 3D holograms that can be viewed through an optical visor and superimposed onto patients, using CT fiducial markers for registration, according to Novarad. For this surgery, the VisAR system projected a 3D hologram of the patient's anatomy onto the patient during surgery, along with a planned target for each piece of surgical software, according to a Novarad press release. By providing real-time guidance, it enabled the surgeon to precisely place the implants required for the fusion procedure, the company said.