Wednesday, December 4 | 3:30 p.m.-3:40 p.m. | SSM15-04 | Room E353B
With the help of artificial intelligence (AI), imaging centers can reduce radiologists' errors and improve quality assurance in chest x-ray interpretations and report generation.Researchers from New Delhi, led by Dr. Vidur Mahajan, associate director of Mahajan Imaging, used an AI algorithm to find cases in which misreads occurred and to make the process of random double reads less tedious for radiologists.
To prove the value of a deep-learning algorithm for quality control, Mahajan and colleagues looked at data from Mahajan Imaging's four outpatient imaging departments.
Workflow evaluation began by applying a basic, high-level binary label for normal and abnormal results. All adult chest x-rays deemed normal were prospectively analyzed through a deep-learning algorithm from South Korean AI firm Lunit Insight that is designed to differentiate between normal and abnormal results.
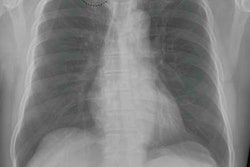
The algorithm provided an abnormality score between 0.00 and 1.00. A chest radiologist then reviewed all images marked as abnormal based on a high sensitivity setting. The sample included 708 chest x-rays marked as normal by radiologists during the one-month study period, while 46 (6%) chest x-rays were labeled as abnormal by the algorithm.
As it turned out, the AI algorithm confirmed that 12 abnormal chest x-rays (24%) showed true abnormalities on review. The 12 cases included lung opacities, apical fibrosis, a cavity, a nodule, and one case of cardiomegaly. Appropriate corrective and preventive actions were taken, and feedback was provided to the radiologists who reported the cases.
Based on the results, a second read with an AI model could help reduce radiologists' errors and speed up reporting, improving patient care in the process, according to the group.