Dear Artificial Intelligence Insider,
The role of artificial intelligence (AI) in radiology needs to be redefined in order to achieve widespread and broad adoption, according to Michael J. Cannavo, aka the PACSman.
In a new column for AuntMinnie.com, he makes the case that AI must be clearly positioned as complementary -- not competitive -- to radiologists. Learn why and how in this edition's Insider Exclusive.
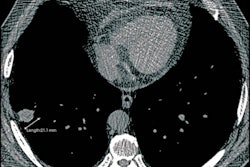
We've also got plenty of news coverage, including a report on how a machine-learning algorithm can predict the risk of malignancy in patients found to have multiple pulmonary nodules during CT lung cancer screening. Also, an AI model was found to deliver a high level of accuracy for characterizing polyps on CT colonography exams, demonstrating potential to significantly enhance the modality's clinical utility.
What's more, AI was able to detect most types of trauma-related findings on pelvic radiographs. It can also help assess hip dislocation risk and measure acetabular component angles on radiographs after total hip arthroplasty.
AI analysis of chest CT exams can predict if COVID-19 patients will need to be treated with steroids, as well as monitor their progression. In addition, new deep-learning models are yielding promising and generalizable results for identifying COVID-19 pneumonia on CT and predicting adverse patient outcomes.
Thanks to an AI-based software application, nurses with no training in ultrasound were able to acquire diagnostic-quality echocardiography images. Also, deep-learning algorithms can detect and quantify aortic valve calcium on cardiac CT exams and predict a patient's risk for future cardiovascular events.
AI is having a positive impact on the teleradiology market, according to a report from Arun Gill of Signify Research. Is AI for image interpretation a friend or a foe to radiologists? A point/counterpoint article series offered two potential visions for radiology's future.
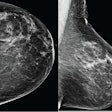
An AI algorithm can outperform other risk-assessment models for predicting the future risk of breast cancer from a mammogram. The combination of AI with Lung-RADS can also sharply increase specificity -- without affecting sensitivity -- in low-dose CT lung cancer screening programs.
A proposal by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to eliminate 510(k) review for a number of AI software applications raised a few eyebrows last month in the radiology industry. AI and radiomics were also able to predict the likelihood of prostate cancer recurrence on multiparametric MRI, enabling preoperative risk stratification of these patients.
Do you have an idea for a story you'd like to see covered in the Artificial Intelligence Community? Please feel free to drop me a line.