CHICAGO - New advancements in its Edison artificial intelligence (AI) program are a major focus in the RSNA 2019 booth of GE Healthcare. The company is rolling out Edison-based tools across multiple modalities, while also highlighting new developments in CT, MRI, interventional, and x-ray.
AI and imaging informatics
Following on last year's launch of its Edison concept for artificial intelligence, GE is showing its progress in baking Edison tools into all areas of the company's operations.
Two of these new tools include Edison Open AI Orchestrator and Edison Open PACS AI. Open AI Orchestrator is designed to simplify the implementation, deployment, support, and scaling of multiple AI applications by integrating AI into the PACS-based radiology reading workflow. GE has demonstrated the tool working with AI applications from iCAD and MaxQ AI.
Another new tool is Clinical Command Centre, a real-time dashboard for managing department operations that GE compares to a NASA command center. GE's goal with the product is to create an "always-on" department where key data are displayed on a "wall of analytics" for experts to monitor.
 Command Control Centre is designed to be the equivalent of a NASA control center for radiology departments.
Command Control Centre is designed to be the equivalent of a NASA control center for radiology departments.Clinical Command Centre pulls hospital data from multiple sources and analyzes it with machine-learning tools to give hospital staff insights into what's happening at a particular moment and also to predict trends and shift resources to meet them.
For example, a tool called Capacity Snapshot gives administrators and managers a look at their department's current imaging capacity; another tool, called Forecast, helps them predict how many beds will be in use at different departments throughout the week. A tool called Imaging Snapshot helps them manage patients by modality, while a module called Clinical Deterioration lets users view how patients have degraded over time.
Users of Clinical Command Centre, such as Humber River Hospital in Toronto, are reporting improved metrics, including faster order-to-scan times. The product is currently available and has been installed at 12 sites.
To spur development of new AI applications, GE has launched Edison Developer Program to make it easier for AI developers to create and implement algorithms on GE systems. GE believes the concept will speed the use of AI and is working with a number of AI firms on different applications, such as an AI quantitative risk assessment tool by Koios that's been built into GE's Logiq E10 ultrasound scanner.
GE has also been expanding its partnerships with provider and commercial players in AI, such as an agreement with Partners HealthCare to deploy deep learning across the continuum of care at the health network's Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham and Women's Hospital Center for Clinical Data Science. There are 15 projects underway across a variety of specialties. GE also has collaborations underway with Saint-Joseph Hospital Foundation in Paris and also Intel.
CT
The latest addition to the GE Revolution product family is Revolution Maxima, a high-performance CT scanner designed to optimize every step of the CT workflow. The new scanner is fitted with a variety of features powered by Edison for advanced applications and AI algorithms.
Most novel among these features is a new patient-positioning system, called Auto Positioning, that is capable of automatically centering individuals undergoing a CT scan with a single click. To perform this task, Auto Positioning uses a depth-sensing camera to generate in real-time a 3D image of an individual lying on the scanner bed. Auto Positioning then uses a deep-learning algorithm to identify the center of the scan range, align it with the isocenter of the bore, and finally center the patient automatically.
The technology aims to improve the accuracy and efficiency of patient positioning and provide the technologist with more time to focus on other aspects of patient care. Early case studies in China have reported single sites scanning roughly 60 patients per day and as many as 17 patients in a single hour.
Revolution Maxima received 510(k) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) earlier this year, though Auto Positioning is still pending clearance.
 The Revolution Maxima is a high-performance CT scanner designed to optimize every step of the CT workflow.
The Revolution Maxima is a high-performance CT scanner designed to optimize every step of the CT workflow.Also in the CT spotlight, Revolution Evo Gen 3 is the third iteration of GE's Revolution Evo CT scanner. The scanner includes GE's deep-learning image reconstruction (DLIR) engine as a software upgrade, which can produce TrueFidelity images characterized by higher spatial resolution and low-contrast detectability. DLIR, which debuted at RSNA 2018, received FDA 510(k) clearance in April of this year and is currently commercially available.
The company also released a new application for Edison called Intelligent Protocoling. The application leverages a proprietary machine-learning algorithm to analyze information from the patient exam order history as well as from specific CT sites to recommend ideal protocols for a particular patient's exam. Intelligent Protocoling continuously learns from patient and site data over time and will eventually be incorporated into GE's Smart Subscription service.
Additional new Edison applications include Hepatic VCAR, which uses a deep-learning algorithm to automate CT liver segmentation in less than 3 seconds, and FastStroke, an application that automatically loads and processes CT scans for stroke workups and then arranges processed scans in an email format.
Women's imaging
For women's imaging, GE is launching Serena Bright, which brings contrast-enhanced biopsy to mammography. Serena Bright allows clinicians to perform breast biopsy with the same mammography equipment used for the screening mammogram, without having to change exam rooms or staff.
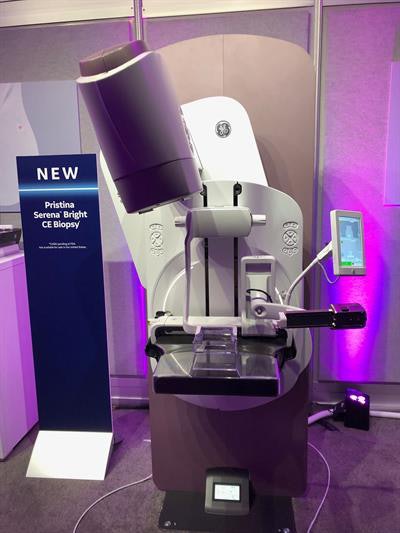 Serena Bright brings contrast-enhanced biopsy to mammography.
Serena Bright brings contrast-enhanced biopsy to mammography.Traditionally, contrast-enhanced breast biopsy relies on MRI. By bringing contrast-enhanced breast biopsy to mammography, Serena Bright now offers a more time-efficient and cost-effective alternative that can be more comfortable for patients. The technology works in conjunction with GE's SenoBright HD contrast-enhanced spectral mammography system and is currently awaiting 510(k) clearance from the FDA.
Also new this year is ProFound AI, an AI-based software application from iCAD that is being shown in GE's booth on the Senographe Pristina. ProFound AI uses an algorithm to detect malignant soft-tissue densities and calcifications in the breast and provide a score indicating the degree of confidence it has in the malignancy of the detected lesion. The resulting score is designed to guide radiologists as they determine whether a suspicious finding will require further workup. Early research has shown that the software can help reduce reading time by approximately 52.7%, as well as increase sensitivity and specificity.
GE is also highlighting its stereotactic biopsy device Pristina Serena and its Pristina Dueta patient-assisted compression remote control device. Pristain Dueta allows patients to manage their breast compression while undergoing mammography with supervision by a technologist. The company is additionally displaying several other previously released products, including its SensorySuite mammography suite for reducing patient anxiety and its Seno Iris Diagnose breast microcalcification visualization tool, among others.
Ultrasound
Released in mid-2019, Venue Go is the most recent addition to GE's Venue family. The point-of-care ultrasound scanner enables clinicians to acquire scans of patients across multiple clinical spaces, from the emergency department to the operating room. Venue Go features a number of AI-powered tools that facilitate the evaluation of ultrasound scans by automating several tasks.
What's more, the scanner comes with a touchscreen that allows for a variety of adjustments during image acquisition. Clinicians can, for example, designate different body regions for scanning and then view all or a selection of the scans on the same screen. The touchscreen can be removed from the dock and is equipped with a kickstand for further mobility.
GE is again showcasing its Logiq E10 ultrasound scanner, which now offers a new AI-based application for automatically obtaining a quantitative breast cancer risk assessment in line with the American College of Radiology Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS). Several other ultrasound products such as GE's Invenia 2.0 automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) system and its Voluson E10 also have new applications on display at RSNA 2019 as well.
Of note, Voluson E10 includes fetalHQ for measuring the size, shape, and contractility of the fetal heart directly on the ultrasound scanner. In addition, Voluson E10 includes an AI-based application, called SonoCNS, that can automatically align three different planar views of the fetal central nervous system into a single view, reducing the number of keystrokes required for fetal brain assessment by an average of 82%.
MRI
At RSNA 2019, GE is highlighting its AIR family of products that deliver clinical and productivity improvements in MRI. One of the newest additions to the line is AIR Recon DL, a reconstruction technique that's based on GE's Edison deep-learning platform.
AIR Recon DL is designed to improve signal-to-noise ratio and sharpness of MR images, producing better images in shorter scan times, according to GE. The algorithm was developed using a neural network trained on thousands of images with the company's Edison platform. FDA 510(k) clearance is pending for the technology for the Signa Premier scanner, and it will be rolled out to other scanners after that.
 AIR Recon DL applies deep-learning reconstruction to improve the sharpness of MR images.
AIR Recon DL applies deep-learning reconstruction to improve the sharpness of MR images.Another new tool, AIR x, is an automated workflow protocol for brain scanning that's designed to improve consistency and productivity. AIR x produces images with less variability, reducing the chance that a patient would have to be recalled due to incorrect slice placement. GE believes technologists will be able to set up exams five times faster with four times fewer mouse clicks using AIR x.
Other MRI tools on display in GE's booth include the company family of flexible AIR radiofrequency coils, such as an anterior array coil that can be wrapped around the patient like a blanket, and AIR Touch, patient recognition software that works with AIR coils to optimize scans and improve workflow.
Interventional
GE is highlighting two new interventional radiology tools for its Discovery IGS platform in its booth at RSNA 2019. One is Embo Assist, which helps interventional radiologists perform complex procedures in the prostate, such as prostate artery embolization. Embo Assist allows users to visualize prostate vasculature and simulate procedures virtually, sparing healthy tissue. The technique is awaiting 510(k) clearance.
Another new tool is AutoRight, which helps users optimize image quality and radiation dose on Discovery IGS systems. AutoRight helps users balance the competing needs of better image quality and lower dose during procedures by adjusting parameters on the fly. AutoRight has 510(k) clearance and will be rolled out for IGS users in 2020.
X-ray
Major highlights in the x-ray section of GE's booth include Critical Care Suite, a family of AI algorithms embedded on the company's Optima XR240amx mobile x-ray system. The tools were recently cleared by the FDA and are designed to help users triage patients, such as by flagging cases that are suspected of having pneumothorax, enabling them to be moved to the top of the worklist.
Critical Care Suite is embedded on the mobile system, a decision that GE made to enable critical patients to be identified and priotized faster. Critical Care Suite also features other tools designed to improve technologist's work, including a tool that automatically rotates images to the correct orientation and tools that perform quality checks on image acquisition protocols such as field-of-view.
In other x-ray news, GE has migrated its VolumeRAD digital tomosynthesis tool to the Discovery XR656 HD radiography room. The company believes that VolumeRAD will help radiologists solve inconclusive studies without sending patients on to additional exams.
Dual-energy subtraction has also been added to Discovery XR656 HD, as well as the Optima XR656 HD, while Helix 2.0 is the latest version of GE's x-ray image enhancement software, with new tools to improve image brightness and contrast, improve contrast enhancement in lung and spine images, and apply noise reduction and bring out fine image details.
Molecular imaging
At RSNA 2019, GE is launching the newest generation of its PET/CT technology, Discovery IQ Gen 2. The system includes enhancements such as Motion Free, a digital respiratory motion management tool that does not use gating devices. Motion Free detects patient movement above a certain level and can alert users to increase image acquisition time to compensate for it.
Another new tool, CadiacIQ Flow, is designed to improve cardiac PET studies by producing functional maps of cardiac blood flow that can be compared with a database of normal images, enabling users to visualize and quantify cardiac PET static, dynamic, and gated images.
 GE has added medium-energy high-resolution collimators to its Discovery NM/CT 870 CZT gamma camera.
GE has added medium-energy high-resolution collimators to its Discovery NM/CT 870 CZT gamma camera.In SPECT, GE is highlighting its Discovery NM/CT 870 CZT gamma camera, based on cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) digital detectors. A new feature on the camera is a medium-energy high resolution and sensitivity (MEHRS) collimator, designed to be used with medium-energy radiopharmaceuticals such as indium-111 and lutetium-177. Both radiopharmaceuticals are seeing increased use, with indium-111 for prostate and neuroendocrine studies and lutetium-177 for theranostic applications, in which the same radiotracer is used for both diagnostic and therapeutic applications.