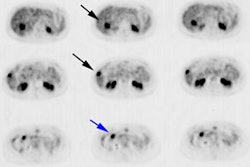
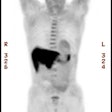
Chest 2000 Dec;118(6):1610-5
The usefulness of positron emission tomography in evaluating patients
for pulmonary malignancies.
McCain TW, Dunagan DP, Chin R Jr, Oaks T, Harkness BA, Haponik EF
Study objective: Positron emission tomography (PET) can contribute to diagnosing and
staging lung cancer, but it has not been determined whether this information influences
patient care. DESIGN: We reviewed the effects of thoracic PET scan results during an
11-month period. For each patient, physicians ordering these scans reported how PET
specifically altered management, and graded the ease of interpretation and overall
usefulness of PET on a 5-point scale. In addition, to appraise general attitudes about
PET, we surveyed 488 national American Thoracic Society (ATS) members and 44 physicians at
our comprehensive cancer center. RESULTS: One hundred twenty-six questionnaires regarding
patients were mailed to 37 ordering physicians, and 98 responses (78%) were returned,
primarily by cardiothoracic surgeons (35%) and pulmonologists (47%). Respondents reported
that PET provided new information in 83 patients (85%) and altered patient management in
64 cases (65%). Major effects on management included decisions regarding biopsy (n = 16),
surgery (n = 16), and palliative treatment (n = 16). Chest clinicians found PET to be more
helpful (4.4 vs 3.9, p = 0.007) and easier to interpret (4.2 vs 3.7, p = 0.025) than other
specialists. Among 139 ATS members (28%) responding to the general survey, 51 members
(39%) had access to PET. PET was more frequently available to university-based (49%) than
community-based (27%) physicians (p = 0.016). The majority of physicians without current
access to PET (69%) indicated that they would like to have it available. ATS members with
access to PET reported that PET results generally affect decisions regarding biopsy or
surgery most often, but found the procedure less helpful than physicians at our center
(2.77 vs 3. 56, p = 0.003) and ordered it less often for lung cancer staging (60% vs 96%,
p = 0.002). CONCLUSION: PET scanning is useful in the management of patients with
suspected thoracic malignancies, but impressions about its roles vary, with PET regarded
more highly where, as at our center, it is used more often. Whether PET alters patient
outcomes requires investigation.
PMID: 11115447, UI: 20567527