Radiographics 2000 May-Jun;20(3):687-98
Diseases of the hepatopulmonary axis.
Meyer CA, White CS, Sherman KE.
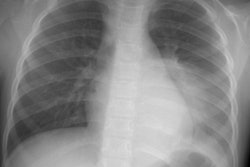
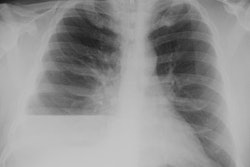
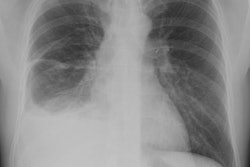
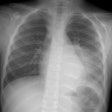
Hepatopulmonary syndrome is the most widely recognized of the processes associated with
end-stage liver disease. Chronic liver dysfunction is associated with pulmonary
manifestations due to alterations in the production or clearance of circulating cytokines
and other mediators. Hepatopulmonary syndrome results in hypoxemia due to pulmonary
vasodilatation with significant arteriovenous shunting and ventilation-perfusion mismatch.
Hepatic hydrothorax may develop in patients with cirrhosis and ascites. Rarely, pulmonary
hypertension occurs in the setting of portal hypertension. A second group of disorders may
primarily affect the lungs and liver (the hepatopulmonary axis). Among these are the
congenital conditions alpha(1)-antitrypsin deficiency and cystic fibrosis. Autoimmune
liver disease may be associated with lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis, fibrosing
alveolitis, intrapulmonary granulomas, and bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing
pneumonia. Sarcoidosis affects the lung and liver in up to 70% of patients. Medications
such as amiodarone can result in a characteristic radiologic appearance of pulmonary and
hepatic toxic effects. Knowledge of these associations will assist the radiologist in
forming a meaningful differential diagnosis and may influence treatment decisions.
PMID: 10835122