Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (Intravascular bronchoalveolar tumor)
Clinical:
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma is a rare neoplasm. All age groups are affected, but 40% of patients are under 30 years of age [1]. Patients are usually asymptomatic or they may present with cough, chest pain, or weight loss [1]. Many tumors will behave in a benign fashion, whereas others are highly malignant. A poor prognosis is associated with airway, vascular, and pleural involvement [1].
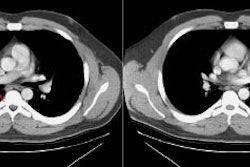
The most characteristic and common finding is the presence of
multiple, small (less than
2-3 cm in diameter), nodules in both lungs in a
peribronchovascular distribution [1,2]. The nodules are usually
well-circumscribed or slightly ill-defined [1]. This pattern is
associated with the best prognosis [2].
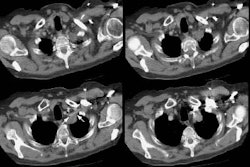
Other patterns of involvement include a reticulonodular pattern,
a parenchymal tumor with pleural invasion, and diffuse pleural
thickening [3]. The reticulonodular pattern is characterized by
multiple reticulonodular opacities associated with interlobular
septal thickening and ground-glass opacities and this pattern can
mimic lymphangitic metastatic disease or interstitial lung disease
[3]. On histopathologic evaluation, the findings are due to
infiltrating nodular proliferation of neoplastic cells within the
lumens of small blood vessels and lymphatic vessels [3].
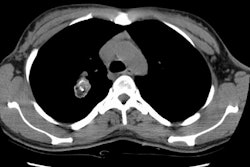
The parenchymal tumor (solitary or multiple) with pleural
invasion is a less common manifestation, but it is associated with
the worst prognosis [3].
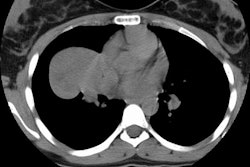
The diffuse pleural thickening pattern is uncommon [3]. The
thickening can extend along the fissures, be associated with a
pleural effusion, and mimic mesothelioma or pleural metastatic
disease [3].
Tumor wedge resection can be performed for patients with amenable
tumor burdens [2]. Patients with slowly progressive disease may
benefit from treatment with celecoxib because of it's
antiangiogenic properties [2]. Sirolimus, a drug which targets the
mammalian target of rapamycin, has also been used with some
success [2].
REFERENCES:
(1) Radiographics 2002; Gimenez A, et al. Unusual primary lung
tumors: a
radiologic-pathologic overview. 22: 601-619
(2) AJR 2020; Jang JK, et al. A review of the spectrum of the imaging manifestations of epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. 215: 1290-1298