Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a distinct subset of MCN that is being recognized with increasing frequency.
1.3 Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm
CLINICAL FEATURES
• Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is a distinct subset of MCN that is being recognized with increasing frequency.
• IPMN was previously referred to by many other names, including duct ectatic mucinous cystadenoma (or cystadenocarcinoma), intraductal mucin-hypersecreting tumor, and intraductal papillary tumor.
• It is characterized by papillary tumor growth and mucin production within the main pancreatic duct, side branches, or both.
• Owing to presumed malignant or premalignant behavior, surgical resection is often considered the treatment of choice.
• Older adults are typically affected, with a slight predilection for males (unlike other cystic pancreatic neoplasms, which predominate in females).
• The clinical picture may resemble that of relapsing or chronic pancreatitis.
• Prognosis is generally favorable in the absence of invasive carcinoma.
IMAGING FEATURES
• Imaging features differ for main duct versus side branch involvement.
• ERCP features of main duct IPMN include a bulging or gaping papilla with extruding mucus, a dilated main pancreatic duct, and intraductal filling defects representing mucin or tumor.
• The imaging appearance of main duct IPMN can mimic chronic pancreatitis.
• Branch duct IPMN most often involves the uncinate process.
• Demonstrating communication of a multicystic lesion with the ductal system is key for diagnosis of branch duct IPMN; MRCP and ERCP may be useful in this regard.
• CT and MR features of invasive carcinoma in IPMN can include marked dilatation of the main pancreatic duct, diffuse or multifocal disease, mural nodules, or a solid mass.
• EUS characteristics include marked ductal dilation, mural nodules, and large irregularly septated cysts; tumors originating from side branches may appear as small clusters of cysts.
FIGURES
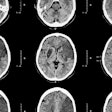
Figure 1.3.2 Pancreas divisum with dorsal duct IPMN.
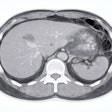
Figure 1.3.3 Side branch IPMN.
Figure 1.3.4 IPMN with invasive carcinoma.
Copyright © 2007 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc.







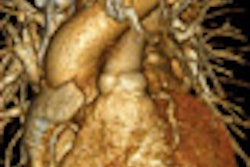





![Images show the pectoralis muscles of a healthy male individual who never smoked (age, 66 years; height, 178 cm; body mass index [BMI, calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared], 28.4; number of cigarette pack-years, 0; forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1], 97.6% predicted; FEV1: forced vital capacity [FVC] ratio, 0.71; pectoralis muscle area [PMA], 59.4 cm2; pectoralis muscle volume [PMV], 764 cm3) and a male individual with a smoking history and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) (age, 66 years; height, 178 cm; BMI, 27.5; number of cigarette pack-years, 43.2, FEV1, 48% predicted; FEV1:FVC, 0.56; PMA, 35 cm2; PMV, 480.8 cm3) from the Canadian Cohort Obstructive Lung Disease (i.e., CanCOLD) study. The CT image is shown in the axial plane. The PMV is automatically extracted using the developed deep learning model and overlayed onto the lungs for visual clarity.](https://img.auntminnie.com/mindful/smg/workspaces/default/uploads/2026/03/genkin.25LqljVF0y.jpg?auto=format%2Ccompress&crop=focalpoint&fit=crop&h=112&q=70&w=112)