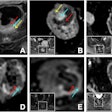
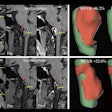
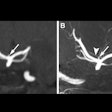
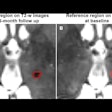
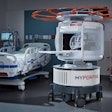
Wellumio, a New Zealand-based medical device company specializing in stroke detection, has enrolled the first patient in a feasibility, safety, and usability assessment of its Axana 0.1-tesla portable MRI device.
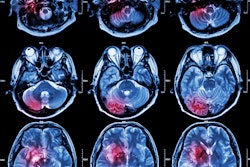
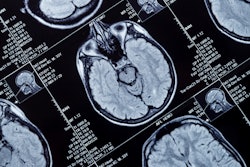
A Melbourne, Australia-based hospital recently used Axana to perform an exam on a 77-year-old woman suspected of acute stroke.
The study will be a two-part, dual-center, feasibility/observational study of the device, with the primary objective being to assess the safety and feasibility of Axana device in a hospital setting with healthy controls and stroke patients. Secondary objectives include evaluating the device's usability, acquiring physiological data from healthy controls and hospital patients, and investigating the reproducibility of MRI scans within and between participants. The research is supported by the Australian Stroke Alliance and managed by Titan Prehospital Innovation, according to Wellumio.
Axana's technology is powered by pulsed gradient-free mapping (PGFM), which eliminates the need for bulky components and allows for the imaging of biomarkers through a portable design ideal for bedside use, the company said.