A flat-panel full-field digital mammography (FFDM) system produced better image quality than computed radiography-based mammography using digital storage phosphor, according to a study from researchers in Vienna, Austria.
The team from the Medical University of Vienna, led by Dr. Gerd Schueller, published their findings in the European Journal of Radiology. The study compared image quality, diagnostic efficacy, and lesion detection of two FFDM technologies, flat-panel FFDM and computed radiography (CR) mammography, in the evaluation of breast lesions (Eur J Radiol, September 2008, Vol.67:3, pp.487-496).
The study included 150 women evaluated between January and June 2003 who had BI-RADS 4 or BI-RADS 5 lesions on prior mammography exams. Each patient had mammography exams with both a flat-panel FFDM unit (Senographe 2000D, GE Healthcare, Chalfont St. Giles, U.K.), and a mammography system (Mammomat 3000 Nova, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany), outfitted with CR storage phosphor plates (Fuji Medical Systems, Tokyo, Japan).
Each of the 150 patients was assigned a breast density category:
- Category A: almost entirely fat
- Category B: scattered fibroglandular densities
- Category C: heterogeneously dense
- Category D: extremely dense
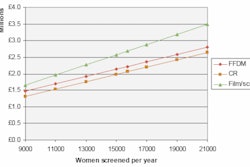
The two techniques categorized the 150 women in the following percentages:
|
"In our study, markedly more breasts were classified with a breast density category of B with FFDM, and, conversely, as a breast density category of C with [CR mammography]," Schueller and colleagues wrote. "We suggest that, most likely, this is due to the observed superior detailed detection of fibroglandular tissue in dense breasts with FFDM, leading to a downward categorization of breast density."
Readers were asked to compare flat-panel and CR mammography images on the following aspects and rate them on a five-point scale, with 1 being excellent and 5 being unacceptable:
- Brightness
- Contrast
- Sharpness
- Noise
- Artifacts
- Detection of anatomic structures, i.e., skin, retromamillary space, glandular tissue
- Detection of calcifications
The researchers found that flat-panel FFDM was rated better than CR mammography for each comparative aspect:
|
The study data showed that flat-panel FFDM and CR mammography were comparable in diagnostic efficacy, with similar sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) figures:
|
But the researchers did find that flat-panel FFDM detected more lesions with calcifications, for a total of 85 compared to the 75 found by CR mammography. They concluded that flat-panel FFDM provides better results in terms of image quality and in finding calcifications than CR mammography.
By Kate Madden Yee
AuntMinnie.com staff writer
October 2, 2008
Related Reading
Austrian study finds FFDM, CR equivalent for breast cancer detection, February 23, 2004
Flat-panel unit beats CR for digital mammography, March 7, 2003
Copyright © 2008 AuntMinnie.com