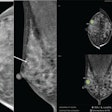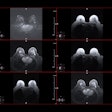
The visibility of screen-detected cancers is generally equal to or higher on synthesized 2D mammography when compared with full-field digital mammography (FFDM), but caution should be used when evaluating asymmetries and lesions less than 2 cm in size, according to a new study published online July 12 in Academic Radiology.
When used with digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), synthesized 2D mammography reduces the radiation dose women sustain when undergoing DBT and FFDM to have a comparison 2D mammography image, wrote a team led by Dr. Sona Chikarmane of Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston. But there are some questions about synthesized 2D mammography in comparison with FFDM.
"Concerns about synthesized 2D mammography include whether [its] image quality is equivalent to FFDM, with the understanding that synthesized 2D mammography is read in conjunction with a DBT dataset," the group wrote. "In addition, only a few studies have looked at the conspicuity and mammographic features of findings on synthesized 2D mammography and FFDM."
To address these clinical concerns, Chikarmane and colleagues investigated the visibility of screen-detected cancers on 2D synthesized mammography from DBT data compared with conventional digital mammography, including 181 cases with cancer identified between October 2015 and June 2017; all cases had FFDM images as well as 2D synthesized mammography images. Three radiologists reviewed the exams and rated them with the following scoring system:
- 1: FFDM more visible than 2D synthesized mammography
- 2: FFDM equivalent to 2D synthesized mammography
- 3: 2D synthesized mammography more visible than FFDM
Of the mammographic features on 2D synthesized mammography, 37.8% were calcifications, 27.8% were masses, 27.6% were asymmetries, and 6.8% were distortions.
The researchers found that 76% of findings were equally or more visible on 2D synthesized mammography compared with FFDM, although calcifications and distortions greater than 2 cm were more visible on 2D synthesized mammography. Asymmetries and masses were less visible on 2D synthesized mammography compared with FFDM.
| Visibility of recalled findings for FFDM and synthesized 2D mammography | ||||
| Finding | FFDM more visible than synthesized 2D mammography | Equal visibility | Synthesized 2D mammography more visible than FFDM | p-value |
| Asymmetry | 48% | 40% | 12% | 0.0014 |
| Calcifications | 8.8% | 19.1% | 72.1% | < 0.0001 |
| Masses | 25.5% | 52.9% | 21.6% | 0.8388 |
| Distortion | 8.3% | 8.3% | 83.4% | 0.0117 |
| Total | 24.3% | 33.7% | 42% | 0.0045 |
Although the majority of screen-detected cancers was identified both on synthesized 2D mammography and FFDM, with some features visualized better on synthesized 2D mammography, the study results suggest radiologists should keep in mind that synthesized 2D mammography has its limitations, according to the researchers.
"Despite the overall maintained conspicuity, we found that 12% of all cases were reassessed as a less conspicuous mammographic feature on synthesized 2D mammography when compared to FFDM," the group concluded. "This finding suggests that radiologists should take caution when assessing one-view findings on synthesized 2D mammography ... when compared to FFDM."