Anonymous, peer-comparison “report cards” were shown to be effective in reducing rates of BI-RADS 3 assessment use and possible overuse, according to findings from a Magna Cum Laude Award-winning online poster presentation at the 2025 American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) annual meeting in San Diego.
After receiving these report cards, radiologists with higher BI-RADS 3 assessments compared with their peers showed significant decreases in use of the category, head presenter Bonmyong “Bora” Lee, MD, and her team from UPenn’s Perelman School of Medicine found.
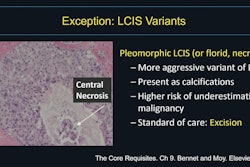
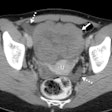
BI-RADS category 3 assessment, reserved for breast imaging abnormalities noted as “probably benign” with a low (< 2%) risk of being malignant, is often overutilized to equivocate a finding, the authors noted.
The research team sent quarterly BI-RADS 3 “report cards” to 38 participating breast imaging radiologists via automated emails over a 17-month assessment period. A recommended target rate of less than 12% for BI-RADS category 3 assessments was given, with Lee and her team offering neither rewards nor punitive measures in the study.
The “report card” included personal BI-RADS category 3 rates for each modality, with all radiologists blinded to others’ individual rates, as well as cumulative rates for the radiologist’s covering site and hospital.
After four cycles, the team reviewed the data using paired t-tests to assess if there were changes in BI-RADS 3 assessment rates either personally or institutionally, Lee said.
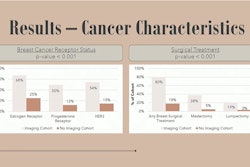
Over the 17-month period, the 38 radiologists gave BI-RADS 3 assessments for 4,289 total patients: 1,171 diagnostic mammograms, 1,281 screening mammograms, 658 MRI, and 1,179 ultrasound exams, with the data showing that the average BI-RADS 3 rate decreased over the course of the period.
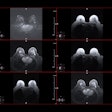
 Radiologists with high initial BI-RADS 3 rates showed a significant decrease between early and late intervention periods; radiologists with low initial BI-RADS 3 rates did not show a significant change early and late intervention periods.Courtesy Lee et al., ARRS
Radiologists with high initial BI-RADS 3 rates showed a significant decrease between early and late intervention periods; radiologists with low initial BI-RADS 3 rates did not show a significant change early and late intervention periods.Courtesy Lee et al., ARRS
While radiologists with low BI-RADS 3 rates before the “report card” assessment didn’t show significant change over the period, those with preintervention BI-RADS 3 rates that were greater than the group median showed significant decreases.