Dear Advanced Visualization Insider,
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) can be a challenging procedure to plan. But 3D-printed aortic root models show promise for improving the planning process, potentially decreasing the risk of postoperative complications.
A group from the University of Minnesota recently detailed their approach, which includes a customized 3D printing process, specialized inks, and integrated electronic sensor arrays. You can read all about it in this edition's Insider Exclusive.
Meanwhile, 3D printing was also found to be useful in helping to plan surgeries for complex cases of congenital heart disease. Researchers from the University of Ulsan in Seoul, South Korea, found that 3D-printed models improved surgical confidence and even led to a change in strategy in some patients.
In other news, virtual imaging trials may be able to help guide the best use of imaging in detecting and monitoring COVID-19, according to new research from Duke University. Also, a Louisiana State University group has created 3D digitally segmented models that demonstrate the extent and distribution of COVID-19 in patients.
Augmented reality (AR) continues to show utility in radiology education. A program at Case Western Reserve University found that a holography education project led to much higher anatomy test scores for medical students on anatomy tests -- even eight months later. In addition, AR and 3D CT holograms can significantly improve the performance of first-year medical students for recalling head and neck anatomy, according to a group from the University of Pennsylvania.
But AR technology also shows promise in other applications, including as an alternative to traditional MR console software for controlling MR scanners. Another Case Western study detailed how a gesture-based AR interface could enable operators to control MR scanners wirelessly and visualize images in 3D, all while keeping the patient in direct sight.
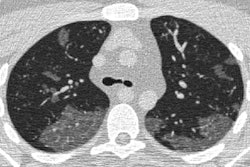
Radiomics features on noncontrast-enhanced CT exams can be used to help identify which patients with COVID-19 pneumonia will need to be admitted to the intensive care unit, as well as predict outcomes. What's more, radiomics can be utilized to predict stroke treatment success, non-small cell lung cancer patient outcomes, and interstitial lung disease survival. It can also improve CT lung cancer screening and assist in differentiating between benign and malignant axillary lymph nodes in women with breast cancer.
Is there a story you'd like to see covered in the Advanced Visualization Community? Please feel free to drop me a line.