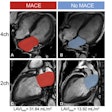
The RSNA is planning to launch a new Quantitative Imaging Committee (QUIC) with the goal of expanding its quantitative imaging initiatives into areas not currently reached by the Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers Alliance (QIBA).
The new committee will seek to build on the success of the QIBA, an initiative aimed at implementing quantitative imaging in clinical trials and clinics.
"The committee structure broadens the charge of RSNA's quantitative imaging efforts beyond biomarker profiles," said Carolyn Meltzer, MD, RSNA Board of Directors liaison for science, in comments to AuntMinnie.com.
Quantitative imaging is defined as the extraction of quantifiable features from medical images "for the assessment of normal or the severity, degree of change, or status of a disease, injury, or chronic condition relative to normal," according to RSNA.
Ultimately, establishing standardized quantitative imaging methods can enhance the accuracy of medical imaging and improve how patients are diagnosed and treated, proponents suggest.
RSNA launched QIBA in 2007, with periodic reviews evaluating its progress. After in-depth study of the 2022-2023 review, the RSNA Board of Directors voted to modify its current infrastructure, a more loosely defined collaborative network.
Over the past several years, QIBA's efforts have reduced variability across devices, sites, patients, and time, with recent so-called "QIBA Profiles" being implemented in sports medicine, cancer, and interventional radiology, noted Melzer, dean of the dean of the Keck School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles.
Innovations in radiomics and AI have recently moved to the forefront in quantitative imaging in radiology, she said, and the new infrastructure will include direct participation and feedback from relevant stakeholders and focus on specific use cases.
Specifically, the Quantitative Imaging Committee (QUIC) has been charged with the following:
- Creation of a mechanism whereby imaging profiles can be submitted by outside entities for RSNA endorsement
- Oversight of one to three biomarker committees selected for their clinical trial/clinical care applicability
- Education of the radiology community about the importance of quantitative imaging, availability of QI Profiles, and tools to encourage standardization
- Collaboration with imaging organizations and vendors to promote QI and standardization
- Outreach to stakeholders to proactively address end-user needs and advance the adoption of Profiles, including stakeholders from academia, industry, regulatory agencies, patient advocacy groups, and medical imaging societies
- Advocacy to promote the association of QI for AI among RSNA members
The committee's recommendations will be published after a public comment process in peer-reviewed medical journals, as well as in the RSNA's QIBA profile library.
The society is in the process of identifying and soliciting volunteers and verifying appropriate stakeholders, with the transition of activities to the new committee expected by the end of 2023 and new initiatives launched in early 2024, Meltzer said.
"The board is grateful to the volunteers and staff who contributed to the formation of QIBA and who will continue to enhance the value and practicality of quantitative imaging biomarkers to improve patient care," she added.