Dear Artificial Intelligence Insider,
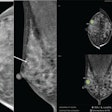
Lung nodules are often hard to characterize on routine noncontrast CT scans, and patients with benign nodules often wind up undergoing unnecessary surgical interventions. The combination of a machine-learning algorithm and a new radiomic feature for lung nodules may be able to help radiologists better distinguish benign and malignant nodules, however.
A multi-institutional group from Cleveland found that the method yielded a promising level of accuracy, and it even outperformed an experienced radiologist and pulmonologist. You can learn all about it in this issue's Insider Exclusive.
Artificial intelligence (AI) also shows much promise for improving the workflow of radiologists, such as helping to reduce the number of interruptions that radiologists face each day. For example, an AI-based chatbot developed at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) can provide evidence-based answers to routine radiology questions from clinicians, physicians, other radiologists, and even patients. Dr. Kevin Seals of Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center shared an update on the chatbot at a recent AI conference in Boston this month hosted by the Insight Exchange Network. You can view our coverage by clicking here.
The Boston meeting also featured an expert panel that delved into AI's evolving role in radiology. While predicting that AI could eventually be all things to all radiologists, the panel members agreed it will take some time to develop, perfect, and validate the algorithms designed to make the technology infallible. What else did the panel members have to say? Click here for our report.
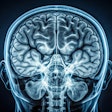
The combination of a machine-learning algorithm and diffusion MRI metrics of brain white-matter infrastructure showed potential for early prediction of working-memory impairment. Click here for all of the details on this research from NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
Speaking of AI and brain MRI, Chinese and U.S. researchers have teamed up to develop a machine-learning algorithm that can analyze MRI scans and predict how well deaf children will be able to develop language skills after receiving a cochlear implant. Click here to learn more.
In addition, Stanford University researchers have concluded that AI may enable PET imaging to be performed using only 1% of the current radiotracer dose levels. How did they achieve this goal? Click here to find out.
Deep-learning algorithms can also analyze PET for signs of dementia and spot large pneumothoraces on chest x-ray exams.
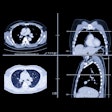
In addition, a deep-learning algorithm that analyzes fractional flow reserve CT scans may help determine which patients suspected of having coronary artery disease should be referred for revascularization. Click here to learn how this algorithm could facilitate better, less-invasive care.
Is there a story you'd like to see covered in the Artificial Intelligence Community? Please feel free to drop me a line.