Infectious Mononucleosis:
Clinical:
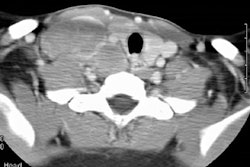
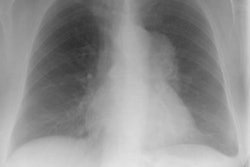
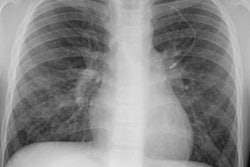
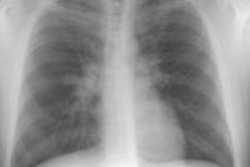
Infectious mononucleosis is an infectious disease associated with the Ebstein Barr virus. Patients are often young adults aged 15-30 years. Patients present with fever, pharyngitis, palpable cervical adenopathy, and an increase in peripheral lymphocytes with a high proportion of atypical cells. Intrathoracic manifestations are UNCOMMON. If intrathoracic disease occurs, the most common manifestation is mediastinal/ symmetric hilar adenopathy (10-13%), while parenchymal infiltrate and effusion are rare. Below the diaphragm, splenomegaly is common. If a lymph node is biopsied, the histology may mimic lymphoma. The polyclonality of the tissue, however, can help confirm a benign process. Since the disease is self-limited, treatment is conservative.REFERENCES: