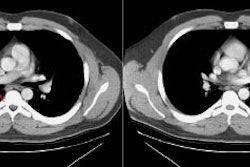
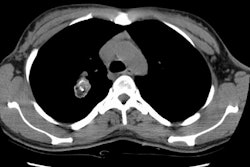
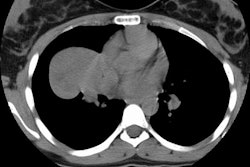
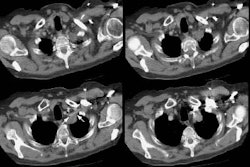
High-resolution CT findings of diffuse bronchioloalveolar carcinoma in 38 patients.
Akira M, Atagi S, Kawahara M, Iuchi K, Johkoh T
OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this study was to analyze the high-resolution CT features of diffuse bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and determine the useful findings in differential diagnosis. MATERIALS AND METHODS: High-resolution CT scans of 38 patients with pathologically proven diffuse bronchioloalveolar carcinoma were reviewed. Sequential CT scans were obtained in 15 patients. The high-resolution CT findings were compared with those of eosinophilic pneumonia (n = 22), multiple pulmonary metastases (n = 12), and tuberculosis (bronchogenic: n = 22; miliary: n = 12). RESULTS: High-resolution CT findings of diffuse bronchioloalveolar carcinoma included ground-glass opacity (n = 29), consolidation (n = 29), nodules (n = 28), centrilobular nodules (n = 26), peripheral distribution (n = 19), and air bronchogram (n = 18). According to the major features, high-resolution CT findings of diffuse bronchioloalveolar carcinoma could be classified into three patterns: predominantly ground-glass (n = 4), consolidative (n = 22), and multinodular (n = 12). Most patients with diffuse bronchioloalveolar carcinoma had a mixture of these findings. The frequency of findings of diffuse bronchioloalveolar carcinoma on high-resolution CT was not different from that of tuberculosis, but the predominant distribution of the nodules and areas of ground-glass attenuation differed between the two. Difference in distribution between bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and bronchogenic tuberculosis included ground-glass opacity remote from the consolidation and a lower lung predominance. CONCLUSION: Although these high-resolution CT findings are not specific, the combination of consolidation and nodules and the coexistence of centrilobular nodules and remote areas of ground-glass attenuation are characteristic of diffuse bronchioloalveolar carcinoma.