Castleman disease of the thorax: radiologic features with clinical and histopathologic correlation.
McAdams HP, Rosado-de-Christenson M, Fishback NF, Templeton PA
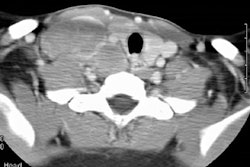
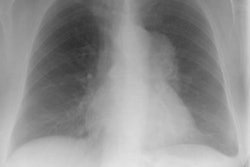
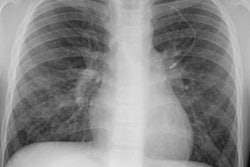
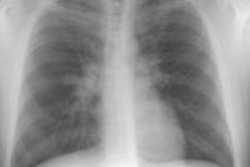
PURPOSE: To correlate the radiologic manifestations of thoracic Castleman disease with the clinical and histopathologic features. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The clinical, surgical, and histopathologic records; chest radiographs; and computed tomographic (CT) and magnetic resonance (MR) images in 30 pathologically proved cases of thoracic Castleman disease were reviewed. RESULTS: Patients with localized Castleman disease (n = 24) typically had the hyaline-vascular type (n = 23), were asymptomatic (n = 14), and had solitary, well-circumscribed mediastinal masses (n = 24). All lesions at contrast material-enhanced CT (n = 13) enhanced. All lesions at MR imaging (n = 5) were heterogeneous and had increased signal intensity on T1- and T2-weighted images. Three patterns were observed on CT or MR images in 20 patients: a solitary, nonivasive mass (n = 10); a dominant infiltrative mass with associated lymphadenopathy (n = 8); or matted lymphadenopathy without a dominant mass (n = 2). Patients with disseminated Castleman disease (n = 6) typically had the plasma cell type (n = 4), were symptomatic at presentation (n = 5), and had bilateral mediastinal masses on chest radiographs (n = 4). At CT, all lesions manifested with diffuse mediastinal lymphadenopathy. All lesions at contrast-enhanced CT (n = 5) enhanced. CONCLUSION: Localized Castleman disease manifests as either a solitary, well-circumscribed mediastinal mass or an infiltrative mass with associated lymphadenopathy on CT or MR images. Disseminated Castleman disease manifests with diffuse mediastinal lymphadenopathy.