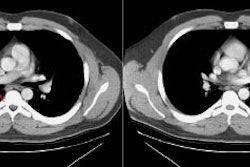
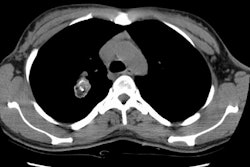
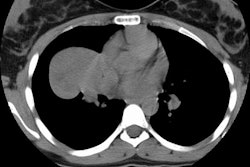
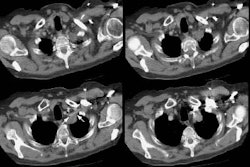
Localized form of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma: FDG PET findings.
Kim BT, Kim Y, Lee KS, Yoon SB, Cheon EM, Kwon OJ, Rhee CH, Han J, Shin MH
OBJECTIVE: The aim of our study was to describe 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose
(FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) findings of a localized form of
bronchioloalveolar carcinoma and to compare those findings with other cell
types of lung cancer. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: FDG PET was performed in 48
patients with lung cancer. The patients had carcinomas of various cell
types: bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (n = 9), squamous cell carcinoma (n
= 11), adenocarcinoma (n = 22), and other cell types (n = 6). Using FDG
PET, we compared peak standardized uptake values among the various cell
types of lung cancer. CT and pathologic findings for patients with bronchioloalveolar
carcinoma were also reviewed. RESULTS: Overall, 48 malignant tumors showed
a mean peak standardized uptake value of 8.0 +/- 4.1. The mean peak standardized
uptake value was 3.5 +/- 2.2 for bronchioloalveolar carcinoma, 10.8 +/-
4.4 for squamous cell carcinoma, and 8.8 +/- 3.2 for adenocarcinoma. The
mean peak standardized uptake value for bronchioloalveolar carcinoma was
significantly lower than that for adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
(p < .001). On high-resolution CT scans, bronchioloalveolar carcinomas
appeared as areas of ground-glass opacity (n = 4), as nodules (n = 2),
as masses (n = 2), and as a ground-glass opacity plus consolidation (n
= 1). On pathologic examination, bronchioloalveolar carcinomas were well
differentiated, having moderate degrees of nuclear atypism, mild degrees
of mitotic figure, desmoplasia, and necrosis. CONCLUSION: The localized
form of bronchioloalveolar carcinoma shows significantly lower peak standardized
uptake values than do other lung carcinomas. Thus, bronchioloalveolar carcinoma
can be a potential cause of false-negative findings of malignancy on FDG
PET scans. When bronchioloalveolar carcinoma is suggested, FDG PET results
should be interpreted in combination with high-resolution CT findings.