Monday, November 26 | 10:40 a.m.-10:50 a.m. | SSC08-02 | Room S402AB
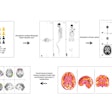
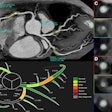
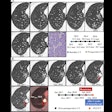
In this scientific session, researchers will describe how a computer-assisted analysis tool can segment and quantify visceral adipose tissue on abdominal CT exams.With the rising incidence of health problems related to obesity and metabolic syndrome, a research team sought to develop a computer-assisted analysis of visceral adipose tissue (CAAVAT) system as an efficient and direct means of analyzing adipose tissue distribution on abdominal CT images, said senior author Marcela Hernández Hoyos, PhD, of the Universidad de Los Andes in Bogota, Columbia.
The study also included researchers from San Ignacio University Hospital in Bogota and the Louis Pradel Hospital of Lyon, France.
Supported by advanced image processing techniques, the CAAVAT system provides reliable quantitative estimates of subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue for diagnostic purposes, risk modeling, and biostatistical analysis in research studies and clinical trials, Hoyos said.
"With the growing concerns over obesity epidemics in the U.S. and other regions of the world, adipose tissue analysis is a key enabling technology to predict the future incidence of cardiovascular disease, stroke events, and metabolic disorders such as diabetes mellitus or dyslipidemia," she said. "Establishing the analysis of adipose tissue as a routine clinical procedure can enable timely prediction and accurate treatment for metabolic-syndrome-related diseases, providing significant improvements to patients' quality of life and savings to the overall healthcare system in the future."