Tuesday, December 1 | 3:10 p.m.-3:20 p.m. | SSJ18-02 | Room N226
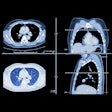
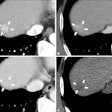
There is still no consensus about the best way to image the posterior circulation in the setting of ischemic stroke, but researchers in Münster, Germany, have found significant value in CT perfusion.Lead researcher Dr. Peter Sporns from Universitätsklinikum Münster plans to report on the high diagnostic value of CT perfusion for detecting posterior circulation stroke, compared with native CT and CT angiography (CTA).
"Our results show a significantly higher detection rate in a large cohort of consecutive patients at our stroke center," he said.
Unlike a couple of smaller prior studies, the study team looked retrospectively at nearly 200 patients with suspected posterior ischemic stroke over three years, adding CT perfusion to noncontrast CT and standard CTA protocols for the detection of ischemia. CT was performed again 19 hours after admission.
A CT perfusion model predicted infarcts in the posterior circulation territory better than other models based on the receiver operator characteristics (ROC) curve -- at 80% for CT perfusion versus 19% for noncontrast CT and 49% for CTA.
CT perfusion detects significantly more ischemic strokes in the posterior circulation than CTA and noncontrast CT alone, the group concluded.
"We therefore recommend implementation of CT perfusion in standard CT protocols," Sporns told AuntMinnie.com.