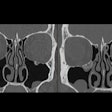
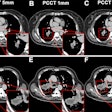
The start in 2020 of Medicare payments for artificial intelligence (AI) software to detect large-vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke on CT scans has precipitated a sharp increase in utilization, according to a new report from group purchasing organization Vizient.
After analyzing its Vizient Clinical Data Base, the company found that 130 hospital members were using the designated code for AI software in LVO detection -- ICD-10-PCS procedure code 4A03X5D -- in the second quarter of 2021, up from 63 hospitals in the fourth quarter of 2020. And the number of procedures also more than doubled.
"AI-assisted stroke triage and workflow platforms appear to be in the early stages of innovation adoption," the authors wrote in volume 4 of Vizient's Medical Device Tech Watch publication. "Currently, hundreds of U.S. hospitals use the technology and thousands of scans are analyzed weekly with AI."
Vizient attributed the rapid adoption to the U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) decision in September 2020 to implement a new technology add-on payment (NTAP) for AI-based detection of LVO stroke on CT angiography exams. Taking effect on October 1, 2020, the NTAP enabled reimbursement up to $1,040 if the total inpatient cost of care exceeds the diagnosis-related group (DRG) payment, Vizient said.
| Growth of AI-based LVO detection software among Vizient members | |||
| 4th quarter 2020 | 1st quarter 2021 | 2nd quarter 2021 | |
| Total procedures using ICD code for AI detection of LVO stroke at Vizient member hospitals | 1,797 | 3,249 | 4,811 |
"Depending on volume and other local factors, NTAP reimbursement may provide substantial revenue to offset technology subscription costs," the authors wrote. "AI usage may also drive revenue growth by increasing the number of mechanical thrombectomies."
Crucially, AI was reported to have played a diagnostic role in approximately 38% of the procedures that resulted in mechanical thrombectomy, according to Vizient.
Five stroke detection algorithms have received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance for LVO stroke detection:
- Viz LVO (Viz.ai), February 2018 via the FDA's de novo pathway
- LVO detection algorithm (Aidoc), December 2019
- Cina Head (Avicenna.ai), June 2020
- Rapid LVO (RapidAI), July 2020
- StrokeViewer LVO (NiCo.Lab), November 2020
The authors expect AI will see continued expansion into many areas of radiology and stroke, according to the authors.
"Faster and more powerful computer hardware, advances in cloud computing, fine-tuning of deep-learning algorithms, and larger training data sets will all contribute to AI's rapid evolution," they wrote.
The authors also noted that dozens of companies worldwide are researching and developing AI-based stroke applications.
"Detection and notification of intracerebral hemorrhage is another high growth application with a number of FDA-cleared AI algorithms," they wrote. "Companies positioned in this space could expand into other stroke applications, like LVO detection, in the near future."