CHICAGO - Toshiba America Medical Systems is offering RSNA 2013 attendees a look at a wide variety of technologies, including an automated CT scanning mode, dose management for interventional imaging, and productivity enhancements in MRI and ultrasound.
CT
Visitors to the CT section of Toshiba's booth are getting a look at a new suite of products called Adaptive Diagnostics that enable Toshiba scanners to adapt imaging scanning protocols automatically based on the biological characteristics of patients.
For example, if a user is preparing a scan on a patient with a varying heart rate, Adaptive Diagnostics would examine the patient's electrocardiogram (ECG) readings over a period of time and would automatically adjust imaging parameters during the scan if the patient's heart rate changes.
Another potential application could be when scanning patients with difficult-to-image body habitus, such as the obese. The scanner would perform two scout images, and then adjust scanning parameters such as tube current, reconstruction method, and filter settings based on the images.
Customers are able to perform manual overrides of settings created by Adaptive Diagnostics, but Toshiba is finding that most early users of the technology are leaving it to run automatically after first adjusting to the noise level they are willing to tolerate in images. The technology also enables Toshiba to implement a dose reduction program at a site in as few as three days.
 Toshiba's Aquilion One Vision CT scanner.
Toshiba's Aquilion One Vision CT scanner.Also a CT highlight for Toshiba is the redesigned Aquilion Prime scanner, which the company introduced two weeks prior to the RSNA meeting.
The second-generation Aquilion Prime can now fit into a smaller room, with a smaller footprint but a larger bore, according to the company. Aquilion Prime now can be sited in a room that's 160 sq ft (14.8 m); the scanner also consumes 30% less power than the older model.
It is also scalable, with users able to start with a midrange 40-slice scanner and upgrade to a 160-slice model later. Toshiba is also touting workflow advantages with the new model, which has better workflow: For example, patients lying prone on the scanner couch can be given breathing instructions on a display.
The new Aquilion Prime now uses the same detector technology as the company's flagship Aquilion One Vision scanner, and it also has Toshiba's advanced iterative dose reduction (AIDR) 3D technology, as well as other applications found on the high-end system.
Toshiba is also introducing metal artifact correction protocols as an addition to the metal artifact management abilities its CT scanners previously had. The new feature has additional functionality to correct for artifacts caused by metal devices that might be implanted in patients.
Finally, Toshiba is also promoting improvements in AIDR 3D reconstruction speeds. Toshiba scanners can now perform AIDR 3D reconstructions at 50 images per second, meaning that a study with 500 images would take just 10 seconds to reconstruct.
Among work-in-progress developments, Toshiba will show improvements in dual-energy imaging functionality.
Ultrasound
Toshiba is reporting strong growth in its ultrasound business over the past year, and in its RSNA 2013 booth, the company is demonstrating technologies designed to keep its momentum going.
These include a new Special Edition version of its Aplio 300 scanner, called Aplio 300 SE. The new model is designed to offer a more fully featured version of Aplio 300, with many optional technologies bundled in that previously had to be ordered on an a la carte basis.
For example, Aplio 300 SE has a larger 19-inch monitor and supports four plugged-in transducers simultaneously, as well as room for more probe holders. The scanner will occupy a price point between Aplio 300 and the flagship Aplio 500.
 Toshiba is showing its Xario 200 ultrasound system.
Toshiba is showing its Xario 200 ultrasound system.
Xario 200 is a new scanner in the Xario product family that will be shown as a work-in-progress, with shipments expected in early 2014. The scanner brings much of the clinical performance of the Aplio systems to the midrange segment, and it includes the same beamformer as well as features such as dynamic tissue harmonic imaging (DTHI), ApliPure Plus, and advanced dynamic flow.
Many of the same workflow features from the Aplio family are available on Xario 200, such as Toshiba's QuickAssist presets that enable sonographers to begin scanning as soon as they place a probe on the patient.
Last but not least, Toshiba is whispering about a work-in-progress technology designed to improve color Doppler imaging of microvasculature. Being developed for Aplio 500, the technology is designed to address a shortcoming of color Doppler in terms of its difficulty in imaging slow blood flow.
Color Doppler traditionally is used for blood flow between 15 cm and 20 cm per second; anything lower produces artifacts and noise, making the mode less useful for small vasculature. However, the new technology makes color Doppler viable at flows as low as 1 cm to 3 cm per second, enabling users to visualize vessels as small as 1-mm wide.
MRI
Key highlights in the MRI section of Toshiba's booth are new technologies and sequences that put additional clinical flexibility into the hands of Toshiba customers.
Two new advanced visualization techniques are cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) dynamic imaging (CSF Dynamic) and 3D arterial spin labeling (ASL) imaging. CSF Dynamic is a proprietary Toshiba technique that enables the visualization of spinal fluid movement using TimeSLIP, a noncontrast technique that's safer for patients.
Meanwhile, 3D ASL looks at blood flow and perfusion characteristics of the entire brain, and it can be performed without contrast in a single scan, unlike other techniques that require multiple scans.
Toshiba is also discussing an upgrade to its M-Power user interface that includes several new features. DirectPath creates exam protocols directly, reducing setup time and pulling patient data directly from a HIS or RIS. Another tool, InScan, automatically performs postprocessing of studies, so when they are delivered to clinicians they are already postprocessed.
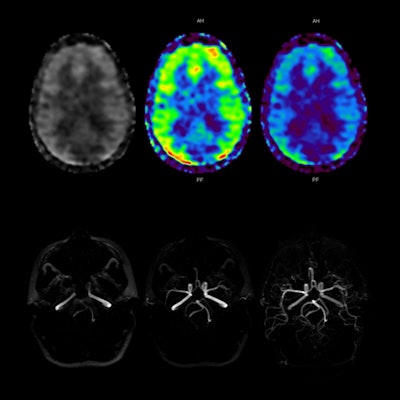 3D ASL perfusion imaging correlates with Toshiba's 3D ASL MR angiography technology to demonstrate uniform filling of both brain hemispheres. Image courtesy of Toshiba.
3D ASL perfusion imaging correlates with Toshiba's 3D ASL MR angiography technology to demonstrate uniform filling of both brain hemispheres. Image courtesy of Toshiba.Another M-Power feature, EasyTech, is designed to standardize difficult exams such as cardiac MRI studies, enabling the production of repeatable exams with consistent image quality.
On the hardware side, Toshiba is spotlighting a new 16-channel Flex SPEEDER coil for its 1.5-tesla scanners that can be placed closer to patient anatomy, improving signal-to-noise ratio. Another new item is a 32-channel head SPEEDER coil that delivers better image quality and supports diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) and functional MRI.
Finally, Toshiba is pointing to customer experiences with the Rapid Transport System (RTS) that it debuted at the 2012 RSNA conference, which is based on a tray that rests on a gurney. Patients can be prepared for a scan on the tray outside the MRI suite, then wheeled up to the scanner and deposited on the patient couch.
The system improves efficiency for imaging facilities and is an improvement over the scanners that have detachable tables. One Toshiba customer found that the system saved the facility four patient moves each day.
Also, Toshiba is celebrating the 15th anniversary of its Pianissimo MRI noise reduction technology.
X-ray
Flexibility is a major highlight in the x-ray section of Toshiba's booth at this year's meeting. For example, the company is introducing a new configuration for its RadRex-i general-purpose digital x-ray system that uses a single wireless digital detector rather than the two-panel version highlighted at RSNA 2012.
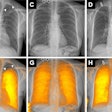
 Lateral cerebral digital subtraction angiography image acquired using Infinix VF-i biplane system, showing a large arteriovenous malformation. Image courtesy of Toshiba.
Lateral cerebral digital subtraction angiography image acquired using Infinix VF-i biplane system, showing a large arteriovenous malformation. Image courtesy of Toshiba.
While most x-ray rooms typically have a fixed detector in the table and another detector in the bucky stand, the new model replaces that configuration with a single 7-lb detector that can be moved back and forth. The configuration offers a more affordable option for customers, according to the company.
Interventional
Radiation dose reduction has become a huge issue in medical imaging, especially in interventional imaging. To address dose concerns, Toshiba is launching its Dose Tracking System (DTS), a dose management tool for its Infinix line of angiography systems.
DTS offers a twist on radiation dose measurement: It tracks dose at the skin surface, rather than in the air kerma or what's delivered to the device table. The system offers a visual look at radiation dose during exams, with users able to see where x-rays are hitting patients. Color-coded indicators move from green to yellow to red, indicating to healthcare personnel that it could be time to reposition the patient.
DTS will be offered on all the systems in the Infinix line; it has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance and will be commercially available this year.
Another interventional imaging enhancement for Infinix is a spot fluoroscopy mode that uses asymmetrical collimation. Other angio systems use a symmetrical collimation in which both collimator planes move at once, producing a small focused image on a black screen. The new spot fluoro mode embeds a larger field-of-view onto the last image hold, giving clinicians a better idea of their location in the patient.
Finally, Toshiba will introduce a version of the Kalare radiography/fluoroscopy system that replaces the unit's image intensifier with a 17 x 17-inch flat-panel digital detector. The new system will be available in the first half of 2014.