VIENNA - In the past, ECR languished in the shadow of Chicago's RSNA show when it came to new product introductions. But ECR is slowly coming into its own, as indicated by new product launches from the major multimodality companies at this week's congress.
Siemens Healthcare, GE Healthcare, Philips Healthcare, and Toshiba Medical Systems are all giving ECR 2014 attendees a look at new technology on the conference exhibit floor. While some of these systems were the traditional European launches of scanners first seen at the RSNA show, a number of them were products specifically developed for the European market -- and were being seen for the first time at ECR 2014.
Siemens
This German multimodality vendor made Somatom Scope an ECR 2014 highlight, with the CT scanner making its global debut at the conference. The 16-slice scanner is designed for budget-conscious sites, with a particular emphasis on low total cost of ownership: as much as 35% lower.
To accomplish those savings, the system includes a number of technologies, bundled together into what Siemens is calling eCockpit, that were developed to reduce operating costs. These include eMode, a scanning mode that runs the generator and gantry at lower power settings; eSleep, which puts the system into a "sleep" mode that reduces power consumption when the system isn't being used; and eStart, which avoids "cold" starts of the scanner by warming up the x-ray tube in advance.
In fact, Siemens is making Scope even more attractive to imaging sites by offering a special service plan in which users can reduce their maintenance costs based on how much they use all three scanning modes. The company is able to verify usage through scanner logs.
Early installations of Scope have been made in Portugal and China. Siemens plans to begin shipping the scanner in Europe in the middle of 2014.
Other Siemens ECR 2014 highlights include Somatom Force, the company's flagship CT scanner first launched at RSNA 2013, and syngo.via VA30, a new version of the company's advanced visualization software that includes General Engine, a reading and reporting mode.
Ysio Max is a new digital radiography system that was also launched in Chicago and that received the CE Mark in March, clearing the way to shipments in two months. Siemens is highlighting the flexible configurations available with the system, from a static 43 x 43-cm detector to a wireless portable version and a small-format configuration with a 30 x 24-cm detector.
The company also used a giant-sized floor model of a liver to demonstrate its FreezeIt technique, an MRI scanning protocol that reduces motion artifacts and eliminates the need for patients to take breath-holds during liver exams.
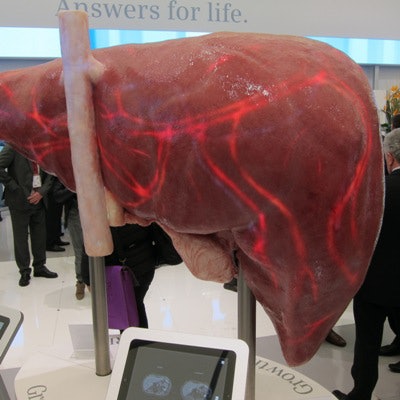 This gigantic liver illustrates FreezeIt, an algorithm from Siemens that allows MRI scanning of the liver without patient breath-holds.
This gigantic liver illustrates FreezeIt, an algorithm from Siemens that allows MRI scanning of the liver without patient breath-holds.GE
GE is making its new Dose Blueprint radiation dose reduction initiative a major focus at this year's congress.
Dose Blueprint combines CT dose reduction technologies such as iterative reconstruction with dose tracking software to give sites a better idea of the dose their patients are receiving. GE then packages these offerings with consulting services to help hospitals take a more comprehensive and structured approach to facility-wide dose reduction.
At the level of scanning protocols, GE said that sites can use technologies like its adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction (ASIR) to reduce dose dramatically when scanning. Then, the vendor's DoseWatch software can be employed to track patient dose on an ongoing basis. Finally, Dose Blueprint calls for a continuous improvement process with GE consultants dispatched to hospitals to implement dose reduction protocols.
This last topic is a key component of Dose Blueprint, as an effective radiation dose reduction program often requires hospitals to do more than change their scanning protocols -- they must change their operating culture. For example, hospitals may make a good initial effort at dose reduction by adopting new scanner settings, but then alter them as time goes on to achieve better image quality. Dose Blueprint helps them avoid this to achieve long-term dose improvement.
GE pointed to two major recent dose reduction moves -- the launch of the EuroSafe program at ECR 2014 and the implementation of a new directive to harmonize dose reporting and justification from the European Commission in December 2013 -- as underscoring the company's efforts.
In addition to Dose Blueprint, GE is highlighting its IT activities, including a new program designed to help independent hospitals connect with each other over digital networks. While Europe has many regional healthcare systems that benefit from large healthcare IT networks, there are still a number of hospitals operating independently.
The company's Centricity 360 program enables independent hospitals to exchange and view patient data, allowing them to build interdisciplinary teams from unaffiliated institutions. Specific use cases could include a trauma patient who has data at one institution, but who is being seen in the emergency room at another site.
The program is based on GE's Predix industrial Internet software, and the company has built a data center in San Ramon, CA, in the U.S. to support the program. The initiative is being launched first in the U.S. and France, with the first customers coming online in the second quarter.
Big iron has always been a GE forte, and ECR 2014 is no exception. The company is giving ECR attendees a look at the Revolution CT scanner launched at RSNA 2013; the system is designed to give users spatial resolution, 16 cm of anatomic coverage per rotation, and dose reduction all in one package. GE expects to receive the CE Mark for the system in the summer, and U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance is pending as well.
GE is highlighting two new Revolution models in its ECR booth: Revolution Evo is a configuration with a narrower 4-cm detector width, while Revolution GSI offers customers a more value-based option for the company's high-resolution Gemstone spectral imaging (GSI) technology.
Finally, GE is giving ECR 2014 attendees an update on the PET/MRI scanner shown as a work-in-progress at RSNA 2013. The system employs a dedicated ring of solid-state PET detectors inside a 3-tesla MRI scanner. Three systems are currently in operation, one at the University of Zurich in Switzerland and two in the U.S., at Stanford University and the University of California, San Francisco.
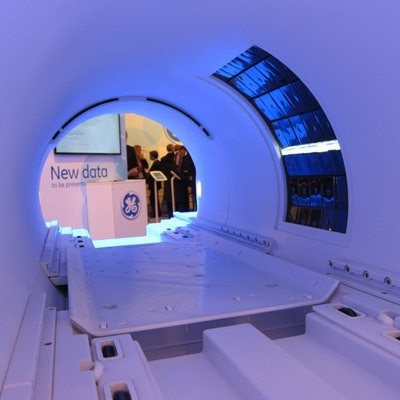 GE is showing ECR 2014 attendees the embedded PET detectors inside its work-in-progress PET/MRI scanner.
GE is showing ECR 2014 attendees the embedded PET detectors inside its work-in-progress PET/MRI scanner.GE plans to offer PET/MRI as an upgrade to its installed base of Discovery MR 750w scanners, as well as offering it as a new system. The company has not yet filed regulatory applications for the system.
Philips
Philips is promoting products first introduced at RSNA 2013, in addition to scanners that are making their global debut at ECR 2014.
Among the latter is the new Ingenia CX line of MRI scanners. The 1.5- and 3-tesla scanners occupy a lower price point than the firm's flagship Ingenia systems. The CX magnets sport 60-cm bores, compared with 70 cm on the premium units, but utilize the same dStream digital broadband architecture found on the more expensive systems.
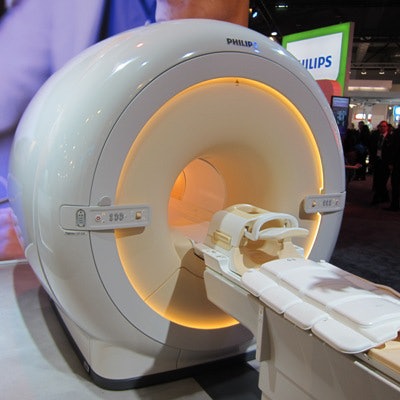 Ingenia CX is a new line of MRI scanners with 60-cm bores.
Ingenia CX is a new line of MRI scanners with 60-cm bores.Philips was able to cut manufacturing costs with the smaller bore widths, and the company pointed out that some users prefer 60-cm bores as radiofrequency coils are closer to patients, which has the potential to improve image quality.
The Ingenia CX scanners have received CE Mark and FDA 510(k) clearance, and are currently shipping.
In other MR news, Philips is discussing therapeutic techniques that are available for use with its scanners in Europe, such as MR radiation therapy planning, Sonalleve MR-HIFU (high-intensity focused ultrasound), and Ingenia MR-OR intraoperative MRI technology.
In radiography, a technology seen at RSNA 2013 that Philips is talking up this week is SkyFlow, a new algorithm for digital radiography that removes scatter radiation, enabling users to acquire mobile radiography images without a grid. This can reduce the number of retakes that are required due to grid cutoff, according to the company.
SkyFlow was developed for Philips' MobileDiagnost wDR unit; the company is also releasing a new cassette-sized 24 x 30-cm SkyPlate flat-panel detector (the previous digital detector on the unit wasn't cassette-sized). The new panel uses Secure Wi-Fi to transfer images, which can reduce the risk of infection due to cables.
SkyFlow is being offered as an upgrade for the company's large installed base of radiography systems; the company is also offering a SkyFlow Pro package that includes the digital detectors as well as an Eleva workstation.
On the imaging informatics side, Philips is discussing IntelliSpace Portal 6, the next generation of its advanced visualization and image analysis software. The new version has better clinical coverage and streamlined workflow, and configurations are available that support the ability to review and analyze images from multiple vendors.
Toshiba
Like the other multimodality vendors, Toshiba is demonstrating a mix of brand-new technologies and products seen previously at RSNA 2013.
Among the new introductions is a faster version of its Astelion/Advance 16-slice multislice helical CT scanner, with a souped-up gantry speed of 0.6 seconds per rotation. The faster speed reduces breath-holding time and contrast agent volumes, and offers support for a wide range of clinical applications -- such as cardiac calcium scoring and lung volume analysis, according to Toshiba.
The company is also highlighting the next generation of its Aquilion One flagship CT platform, launched at RSNA 2013, and reported that it is beginning to record European installations.
Toshiba is also discussing a new interventional suite concept that combines an Aquilion One CT scanner on rails with an Infinix-i angiography system. The company believes the configuration will be useful during interventional procedures when a 3D CT scan could help guide therapy.
Another interventional technology on display is Dose Tracking System (DTS), which enables users to follow radiation dose during procedures with an easy-to-read color-coded dashboard. DTS provides on-the-spot dose monitoring, and it can provide alerts to users if certain thresholds are exceeded.
The company's Ultimax-i multipurpose radiography/fluoroscopy system is now available with an overhead tube conveyor and vertical tube stand for better flexibility in cases where a source-to-image distance greater than 120 inches is desired. The company is also demonstrating its RexPanel, which adds wireless capability to its RadRex-i DR system.
In ultrasound, Xario 100 is a new budget-oriented version of its Xario 200 scanner. Unlike Xario 200, the new model lacks a touchscreen display, and it also doesn't have many of the bells and whistles that are offered standard on its big brother. Xario 100 is designed for a full range of clinical applications, including musculoskeletal, vascular, ob/gyn, and cardiac imaging. The system is shipping.
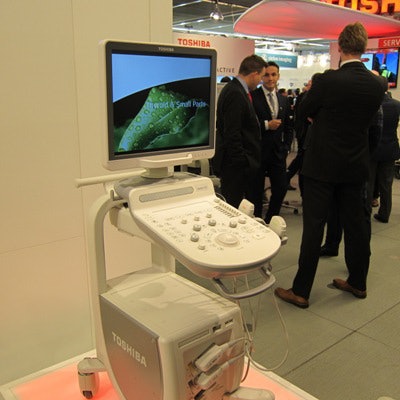 Xario 100 is a new budget-priced ultrasound scanner from Toshiba.
Xario 100 is a new budget-priced ultrasound scanner from Toshiba.Finally, Toshiba is reprising for Europe its launch of the Vantage Elan MRI system first shown at Journées Françaises de Radiologie (JFR), the French national radiology congress. The company is promoting the fact that the unit sites in spaces as small as 23 square meters, while having the same image quality as other 1.5-tesla scanners.
Vantage Elan features a 64-cm bore and is designed for lower overall total cost of ownership. The system is entirely water cooled, and it can be sited without the need for a separate technical room or air conditioning system. Two scanners have been installed in Japan; none have been sited in Europe yet.