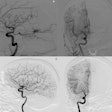
Researchers at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago have found quantitative MR angiography (QMRA) to be a promising screening tool for detecting in-stent stenosis with high sensitivity and specificity.
QMRA uses conventional MRI to produce a 3D model of the vasculature and quantify vessel blood flow. The procedure is noninvasive and does not require contrast agents.
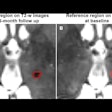
The retrospective study evaluated 14 patients who underwent stent placement for cerebral aneurysm or intracranial stenosis. All patients had a QMRA scan performed within one year after stent placement and a follow-up diagnostic angiography study within one month of the QMRA scan.
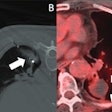
The study found that low blood flow as measured by QMRA at sites of intracranial stent placement was significantly associated with in-stent stenosis by catheter-based angiography.
The researchers also noted that QMRA was 100% sensitive and able to detect narrowing of stented arteries in all cases where invasive angiography showed greater than 50% stenosis.
Due to the small study sample, the researchers suggested larger prospective studies to confirm their findings. The study is available early online and will appear in the March issue of Stroke.
Related Reading
CMS launches national coverage analysis of cardiac MR flow studies, January 22, 2009
AHA urges cautious use of coronary CTA and MRA, July 9, 2008
Cardiac MR measures predict pulmonary hypertension, April 9, 2007
MR angiography offers greater detail in vascular imaging, March 10, 2006
4D MRI enables blood-velocity measurement in mitral valve insufficiency, June 24, 2005
Copyright © 2009 AuntMinnie.com