Contrast agent developer NanoScan Imaging of Lansdale, PA, is drawing attention to results of a new research study in the Journal of Nuclear Medicine regarding its N1177 agent.
N1177 is an emulsified suspension that's composed of crystalline iodinated particles dispersed with surfactant. NanoScan is developing the agent for use with CT angiography to visualize blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. N1177 also accumulates in macrophage cells, allowing for their detection with CT.
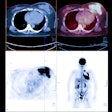
In a study published in the June issue of JNM, researchers from the Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York City investigated whether or not N1177 correlated with macrophage activity evaluated with FDG-PET. After only two hours, the enhancement of macrophage-rich plaque after the injection of N1177 was significantly higher and specific inside the vessel walls of rabbits fed a high-cholesterol diet compared to control rabbits fed a normal chow diet.
In addition, the intensity of enhancement in the aortic wall measured with CT after injection of N1177 correlated with both FDG uptake on PET/CT and macrophage density on immunohistology, the company said. The results suggest that N1177 can be used for the identification of high-risk atherosclerotic plaque with CT.
Copyright © 2009 AuntMinnie.com