CHICAGO - A new 3-tesla MRI magnet, a molecular breast imaging (MBI) system, a hybrid PET/CT MR suite, and a wireless digital radiography (DR) detector are among the highlights in the booth of GE Healthcare of Chalfont St. Giles, U.K., at this week's RSNA meeting.
MRI
Called Discovery MR750w, the new scanner features a new design and compact superconducting 3-tesla magnet with active shielding and zero cryogen boil-off, according to the company. The scanner also features a 70-cm diameter bore and gradients rated at 44 mT/m amplitude and a 200 T/m/sec maximum slew rate.
 |
| GE's MR750w scanner with GEM Suite. |
In addition, GE's acoustic reduction technology (ART) reduces scanner noise, while MultiDrive radiofrequency (RF) coils improve image quality for abdominal imaging and enable users to change phase and amplitude independently. MR750w is pending 510(k) clearance with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and is being shown as a work-in-progress.
GE's older wide-bore 1.5-tesla scanner, Optima MR450w, has received a makeover to match its 3-tesla sibling. What's more, both scanners have received GEM Suite, a new set of receive-only RF coils that can be used individually or combined for 205 cm of total scan coverage. GEM Suite has 160 coil mode configurations, and the system can auto-select the most appropriate coil for the clinical indication. The suite also includes patient comfort features such as feet-first imaging. GEM Suite is pending 510(k) clearance.
Also getting a makeover is the extremity MRI scanner that GE acquired when it bought ONI Medical Systems in November 2009. Now called Optima MR430s, the redesigned system features a 1.5-tesla superconducting magnet with gradients rated at 70 mT/m amplitude and a 300 T/m/sec slew rate. Optima MR430s is also awaiting 510(k) clearance.
On the clinical applications side, GE is touting Propeller 3.0, the newest release of its motion correction software; 3D ASL (arterial spin labeling) for quantitative brain perfusion assessment; and MR-Touch, an MRI elastography application.
Molecular imaging
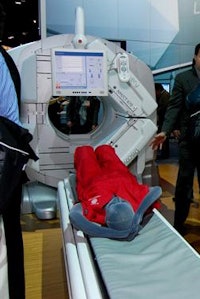 |
| The Discovery NM/CT 670 scanner. |
GE is calling the hybrid suite PET/CT+MRI, and the company has installed the first unit at University Hospital Zurich in Switzerland. First announced at the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM) meeting last month, the suite incorporates a mobile patient table stationed between a PET/CT scanner and an MRI system. The table is able to shuttle patients between scanners without requiring them to change positions or get off the table, and images are fused during reconstruction.
GE believes the approach is more economical than competing solutions that incorporate a PET detector array inside an MRI gantry, and that it give customers more flexibility with future upgrades. Patients can also be scanned independently on either system.
The MBI system, called Discovery NM750b, includes a cadmium zinc telluride (CZT) digital detector with a small field-of-view that's designed for dedicated breast imaging based on accumulation of a radioactive tracer, such as technetium-99m sestamibi, in hypermetabolic cancer cells.
GE sees Discovery NM750b as an adjunct to mammography rather than for screening, by providing a secondary imaging technique after an inconclusive primary examination with conventional mammography. The system has received 510(k) clearance and will be available in the U.S. in the second quarter of 2011.
Finally, the company noted that it has made the first shipment in the Americas of its Discovery NM/CT 670 system, which was announced at the EANM show and which combines GE's new Elite NXT detectors, a newly designed SPECT gantry, and a BrightSpeed Elite 16-slice CT scanner. The scanner was installed at Methodist Medical Center in Peoria, IL; it is already shipping in Europe, Asia, and the Middle East. GE also noted that it has installed its 1,500th SPECT/CT unit
Women's imaging
In women's imaging, GE debuted its new SenoBright contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM) technology to aid breast cancer diagnosis by allowing physicians to image blood flow through angiography of the breast using a contrast agent and a dual-energy acquisition technique.
 |
| GE's CESM technology. |
SenoBright uses x-rays at multiple energies to create two separate exposures. These resulting images illuminate and highlight areas where there is contrast uptake and potentially angiogenesis. A CESM exam takes from five to 10 minutes.
Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography is intended to work as an upgrade to GE's Senographe DS and Senographe Essential digital mammography units. SenoBright currently is pending FDA 510(k) clearance in the U.S. and CE Mark approval in Europe.
CT
Reducing radiation dose is a major theme at this year's RSNA show, and GE is highlighting CT technologies designed to dramatically reduce dose.
Earlier in 2010, GE discussed model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR) as the next generation in the company's iterative reconstruction techniques. At this week's RSNA show, GE is taking the wraps off MBIR as a commercial product with the launch of Veo, an MBIR protocol that features lower noise, resolution gain, improved low contrast detectability, and artifact suppression, all at extremely low dose levels.
GE plans to feature Veo on its Discovery CT750 HD scanner following FDA clearance. Veo currently is available in Europe and is pending 510(k) clearance in the U.S.
GE is also talking up ASIR, its first-generation adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction low-dose technology that's available on the Discovery CT750 HD and LightSpeed VCT scanners. ASIR is designed to reduce dose up to 40% to 50% with no loss in image quality, and it can be implemented as an upgrade for existing GE LightSpeed VCT customers.
ASIR, in combination with GE's SnapShot Pulse technology, further helps to reduce dose in cardiac imaging by more than 83%, according to the company. ASIR is now used with more than 600 scanners worldwide.
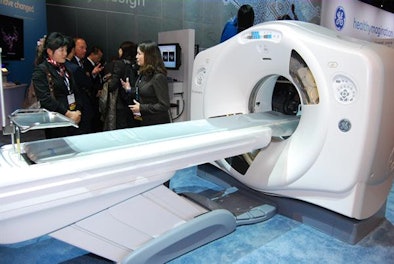 |
| The company's Discovery CT750 HD scanner. |
X-ray and angiography
In a case of fortuitous timing, GE during RSNA week received 510(k) clearance from the FDA for FlashPad, the company's next-generation wireless digital radiography detector.
The battery-operated FlashPad features two handles in a 16 x 16-inch frame, is designed for the company's radiography and fluoroscopy systems, and is able to support advanced applications including VolumeRad, GE's version of digital tomosynthesis for radiography, and dual-energy subtraction, which eliminates overlying bone obstruction from chest or abdominal images.
The company plans to use FlashPad in its Discovery XR656, Optima XR220 amx, and Optima XR200 amx x-ray systems and to incorporate it into a DR imaging option for its Proteus XR/a and Precision 500D products. The use of FlashPad in those systems is pending 510(k) clearance.
GE also displayed its new mobile surgical C-arm, Brivo OEC 850, which recently launched in China, for minimally invasive orthopedic surgery. The C-arm is designed for high image quality for orthopedic and pain management applications at a lower price point. The system will be available for sale in China, Japan, India, Latin America, the Pacific, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. It is pending 510(k) clearance for marketing in the U.S.
In the angiography section of GE's booth, the company is emphasizing dose reduction on its Innova interventional radiology line. The company is highlighting the already low radiation doses produced by Innova systems due to the high detective quantum efficiency (DQE) properties of their flat-panel digital detectors. Innova users can either produce higher-quality images at the same dose, or images of equivalent quality at a lower dose.
Dose reduction technologies that GE is discussing include dynamic range management, which reduces problems with image blackout and burnout by extracting relevant image information, transforming background thicknesses, and then restoring structures of interest. FluoroStore is another dose-saving feature that lets clinicians store fluoroscopy sequences in lieu of high-dose image acquisition modes.
Meanwhile, virtual collimation lets clinicians preview collimator positioning without additional radiation exposure, while InnovaSense is a patient contouring technology that automatically minimizes detector-to-patient distance to help reduce patient skin dose.
Other dose management tools available on Innova include AutoEx, an automated exposure control technique; Innova Dose Personalization; and Innova Dose Reports, which provide an automated way to track system and dose utilization details at the point of care.
Finally, Innova Optima is a new, economical version of the Innova system for developing countries, rural markets, and community hospitals. It employs a single-plane 30-cm digital detector that is flexible enough to perform interventional procedures for both cardiac and radiology applications. The first Innova Optima system has been installed in China.
Healthcare IT
Developing an integrated IT environment across the healthcare enterprise is the focus of the healthcare IT section of GE's booth. The company's efforts are based on its eHealth initiative, and the vendor is making a major push to improve the ability to exchange images and other healthcare data across facilities that may have different PACS networks installed from different vendors.
One example of a technology that can unify such disparate systems is Centricity OneView, which has been installed in Canada for the past two years and is being used as part of an effort to reduce unnecessary transfers of stroke patients through image sharing.
GE is also discussing its participation in a major project under way in France to install a regionwide PACS network in the country's Agence Régionale de l'Hospitalisation d'Ile de France (ARHIF) region, which includes Paris. The installation is the first in a series of projects to move all of France's healthcare facilities to interconnected, filmless operation.
On the PACS side, GE is highlighting Centricity PACS version 3.2, which is designed to enable radiology departments to change the focus of their PACS from a radiology-centric model to one that supports multiple healthcare specialties. Specific features on the 3.2 release include Size Sync, which automatically displays current and prior MR and CT images at the same zoom factor, thus reducing reading time.
The release is available with an optional Web-based diagnostic viewer, Centricity PACS Web Diagnostic 2.0, that enables new radiology reading workflows, according to the company. GE noted that each Centricity PACS installation includes Centricity Enterprise Archive, which is vendor-neutral and standards-based. Version 4.0 of the Enterprise Archive software supports DICOM and non-DICOM images.
For users on the go, GE is demonstrating Centricity Imaging Mobile Access for PACS, which enables Centricity PACS users to pull images and reports from an Apple or Android smartphone or tablet. The application is currently pending 510(k) clearance from the FDA.
New software versions are also being demonstrated for Centricity PACS-IW, the company's Web-based PACS for acute care and ambulatory institutions, and Centricity RIS/PACS-IW, designed for outpatient imaging organizations.
Ultrasound
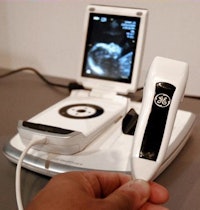 |
| The Vscan pocket-sized scanner. |
In another ultrasound milestone, GE is reporting that it has shipped 3,000 Logiq E9 general imaging scanners since the product was first commercialized in 2008. GE is also touting elastography and needle tracking capabilities with the system, as well as fusion imaging applications.
By Wayne Forrest and Brian Casey
AuntMinnie.com staff editors
November 30, 2010
Related Reading
GE donates Vscan US units for use in Africa, November 18, 2010
Dose reduction to be GE RSNA highlight, November 16, 2010
GE touts Omnipaque taste test, November 10, 2010
GE to continue health academy support, November 9, 2010
GE wins 7T Wis. MRI contract, November 5, 2010
Copyright © 2010 AuntMinnie.com