CHICAGO - RSNA 2017 marks the last year as an exhibitor for one of radiology's most storied brands, Toshiba Medical Systems. But have no fear: The company's products -- including a new superhigh-resolution CT scanner being launched this week -- will appear under the Canon Medical Systems marque starting in January.
Canon acquired Toshiba Medical Systems in December 2016 and plans to rename the division as Canon Medical Systems on January 4. At this week's RSNA meeting, the company is showing Toshiba developments that will soon carry the Canon brand, such as the high-resolution CT scanner, a midtier ultrasound system, and other enhancements and upgrades.
CT
Toshiba made its name in CT with detectors that sport wide-area cover on its Aquilion product line, but at this year's meeting, the company is going another route: extremely high resolution. Aquilion Precision is the platform for the foray, with the new system designed to enable visualization of small structures never seen before in such detail with CT, according to the company.
Current CT technology typically provides 300-micron pixel size and resolution of 20 to 24 line pairs per cm (lp/cm). Aquilion Precision will bring that down to 150 microns and 50-lp/cm resolution, according to the company. It has also made changes to the scanner's image processing chain to support the higher resolution, going from a 512 x 512-pixel matrix to routine reconstruction at 1024 x 1024 pixels, and there is even a superhigh-resolution mode at 2048 x 2048 pixels.
Toshiba made a number of changes to Precision's instrumentation to support the higher resolution, from new detectors with a slice width of 0.25 mm (the current standard is 0.5 mm) to a new x-ray tube that supports six focal spots to adapt to the higher resolution.
What will radiologists be able to see with all that extra detail? In lung imaging, they should be able to visualize ground-glass nodules that are even smaller than what's seen with existing CT technology, while pancreatic lesions that were missed before should now be visible, enabling the detection of cancer at an earlier stage. Toshiba also sees high-resolution applications in the brain and body, while machine-learning applications should get a boost due to the higher level of detail available.
Toshiba is pointing out that because Precision isn't designed for cardiac use, it doesn't have the wide-area detector coverage found on systems such as Aquilion One Genesis; it's a 160-slice system with 4 cm of coverage in 0.25-mm slice widths, versus the 320 detector rows and 16 cm of coverage in 0.5-mm slice widths available on Genesis.
Aquilion Precision is pending 510(k) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA); shipments to U.S. customers should follow in three to four months. Ten systems have been installed at research sites around the world.
In the midtier CT segment, Toshiba is unveiling Aquilion Prime SP, an upgrade of the company's Prime platform in an 80-detector-row package with 0.35-sec gantry rotation speed. A main selling point of the system is that it uses the same PureVision optics found on the superpremium Genesis scanner; these have the ability to filter out low-energy photons to create a harder x-ray beam. Benefits include 19% better low-contrast detectability and 31% less radiation dose, compared with the older model of Prime. The new system also includes Toshiba's variable helical parameters (VHP) protocol.
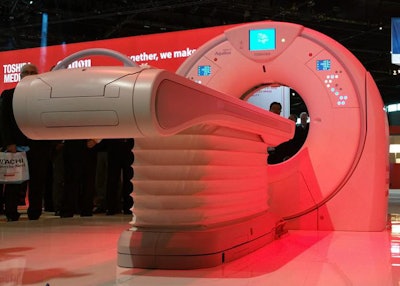 Aquilion Prime SP upgrades the company's Prime system with a new optical chain.
Aquilion Prime SP upgrades the company's Prime system with a new optical chain.Toshiba is also highlighting Aquilion One Genesis, which was launched at the 2016 RSNA meeting. It is designed to offer 16 cm of wide-detector coverage and a 78-cm bore in a package that can be installed in 204 sq ft. In its RSNA booth, Toshiba is discussing the use of filtration to create a harder x-ray beam, as well as its support for the company's First model-based iterative reconstruction (MBIR) protocol, which is being launched this year for head scanning after first being made available for body and lung imaging.
First is being used for stroke patients to perform a noncontrast head scan to look for blood; the same data can then be reconstructed with MBIR for a second set of images to improve low contrast and visualize ischemic changes that can be early signs of stroke.
Finally, Toshiba is showing the third generation of its VHP protocol, VHP3, which enables users to change scan parameters on the fly with a single acquisition. Users can go from gated to nongated and then back to gated acquisitions, or from fast pitch to slow pitch and then to routine pitch. VHP3 protocols have been cleared by the FDA.
Ultrasound
In ultrasound, Toshiba is launching a new package for its iSeries scanners, Aplio i700, i800, and i900. The package includes shear-wave liver assessment for patients with fatty liver disease, which now affects 34% of the U.S. population. One new feature of the package is attenuation imaging, which enables the measurement of how ultrasound propagates into fat, while shear-wave dispersion measures viscosity, another metric for fatty liver disease. Toshiba is also releasing new features for contrast-enhanced ultrasound.
Another highlight is a new product launch at the entry level of its Aplio iSeries premium platform. Aplio i600 makes many features available at a more affordable price point than the i700, i800, and i900 scanners, and at a higher level than the Aplio 500 Platinum.
Aplio i600 will be a shared-services scanner, with applications in cardiology and ob/gyn imaging. All probes found on the 500 scanner can be used on i600, although the system does not support Toshiba's Matrix transducers found on the i700 scanners. FDA clearance for the unit is pending as of RSNA 2017.
In other ultrasound news, Toshiba is launching seven new probes for the iSeries line, including a 22-MHz "hockey stick" transducer for ultrahigh-resolution imaging in musculoskeletal applications such as orthopedics and rheumatology.
Finally, on its midrange product line, Aplio Platinum will have a new version 7.0 release that includes a 21.5-inch monitor, while Xario 200 will get a 6.0 release that includes shear-wave elastography.
MRI
An update for its 3-tesla Vantage Galan 3T MRI platform -- XGO edition -- is occupying the limelight in the MRI section of Toshiba's booth.
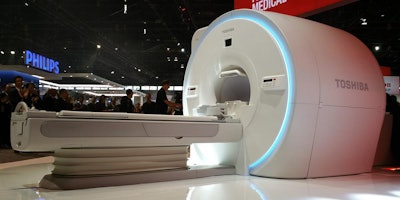 Vantage Galan XGO sports new Saturn X gradients.
Vantage Galan XGO sports new Saturn X gradients.Vantage Galan 3T XGO features several new advances, including Saturn X gradients rated at an amplitude of 45 mtesla/m and a slew rate of 200 tesla/m/sec. The gradients include Toshiba's Pure digital gradient waveform control, which enables users to get a more pure waveform shape when going to maximum amplitude.
For diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), the system has a 23% reduction in the minimum echo time, which confers benefits in DWI scans of the brain and body, such as a 30% increase in signal-to-noise ratio for brain diffusion and up to a 50% improvement in the liver.
Another major component of the XGO release is multiband SPEEDER, Toshiba's family of parallel imaging technologies. Multiband imaging allows the acquisition of up to two slices at a time for DWI studies.
A third component of XGO is cardiac sequences that were added to the Titan Zen scanner over the summer. These include a T1 mapping sequence for cardiac mapping and phase-sensitive inversion recovery (PSIR) for cardiac imaging at 3 tesla. 510(k) clearance is pending for the XGO package.
In other MRI news, Toshiba is showing a laser alignment system for patient positioning in radiation therapy planning studies.
Finally, on the advanced visualization side, the company is demonstrating capabilities now available through Toshiba's acquisition of French software developer Olea Medical in 2015. The company has developed the ability to perform synthetic contrast exams from two short input MRI scans with its Olea Nova+ software; the first applications for the technique will be in the head, with other areas to follow.
X-ray/vascular imaging
In this area, Toshiba is highlighting strides the company has made in its Infinix-i 4DCT program, which combines a CT scanner on rails with an interventional radiology suite for added flexibility in interventional procedures. The version Toshiba is showing on the RSNA floor combines an Aquilion One Vision scanner with an Infinix-i Sky angiography system.
 Toshiba has integrated a CT scanner on rails with its Infinix-i Sky angiography system.
Toshiba has integrated a CT scanner on rails with its Infinix-i Sky angiography system.Currently, Toshiba has three 4DCT sites installed, with one more going in after RSNA 2017. The company is highlighting the system's ability to plan, treat, and verify with lower cost and enhanced patient safety, as patients don't need to be moved from one room to another. At the RSNA show, Toshiba is talking up the 16 cm of organ coverage available on the CT component, along with its use for neurological applications.
 Toshiba has integrated a Canon overhead x-ray tube system with its Ultimax-i R/F system.
Toshiba has integrated a Canon overhead x-ray tube system with its Ultimax-i R/F system.For the company's Ultimax-i radiography/fluoroscopy (R/F) system, Toshiba has added an overhead tube and wireless digital x-ray detector from corporate parent Canon, making the system a true multipurpose room that can now perform static chest studies. The system represents the first integration of Toshiba and Canon technologies, according to the company.