The American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) has published best-practice guidelines to improve the safety and effectiveness of image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) treatments. The white paper, part of ASTRO's target safety campaign, was published online April 17 in Practical Radiation Oncology.
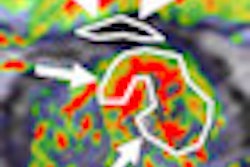
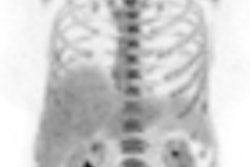
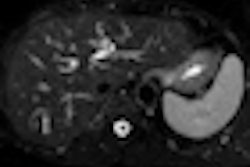
IGRT systems identify the location of a target tumor and normal tissues so that highly conformal dose distributions, higher dose prescriptions, and shorter fractionation treatment schedules for patients can be implemented. Imaging is performed on a fraction-by-fraction basis.
When IGRT is used, there needs to be strong integration between IGRT practices, planning target volume (PTV), and the design of a patient's treatment protocol. IGRT techniques can substantially reduce geometric positioning areas that can occur between treatment planning and delivery.
To ensure safe, high-quality radiation therapy treatment using IGRT technologies, the document focuses on developing protocols for image acquisition and interpretation, ample and continuing education and training, and development and continuous performance of quality assurance protocols and practices.
Emphasis is also placed on constant communication between an IGRT team that includes radiation oncologist, radiation therapists, medical physicists, and medical dosimetrists.
The white paper describes in detail 10 foundational elements for safe and effective IGRT practices. It may be accessed free of charge here.