Patients who received breast brachytherapy delivered with a strut-based applicator had low recurrence rates and minimal toxicities four years after treatment, according to a presentation at last week's American Brachytherapy Society (ABS) meeting.
Dr. Catheryn Yashar, associate professor of radiation medicine and applied sciences at the University of California, San Diego, reported on the outcomes of 101 women in the multisite study with a median follow-up of 48.3 months.
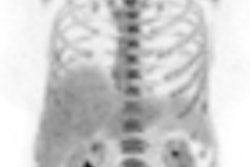
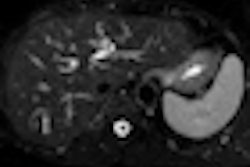
All patients had been treated at one of three cancer centers with accelerated partial-breast irradiation (APBI) using a Strut-Adjusted Volume Implant (SAVI) applicator (Cianna Medical). The applicator can be expanded to conform to the site of a tumor cavity and a patient's specific anatomy.
The patients received a conventional dose of 3.4 Gy delivered in 10 fractions twice a day. Of the group, 71 had invasive disease and 29 had ductal carcinoma in situ. Most (83%) were postmenopausal, and the median age was 62 years. Median tumor size for the group was 12.5 mm (range, 2-35 mm).
Local control was excellent, with a recurrence rate of 2%, according to Yashar. Grade 2 or greater post-treatment toxicity included seroma (2%) and telangiectasias (2%). No patients experienced hyperpigmentation or fat necrosis. Breast asymmetry secondary to radiation effects occurred in 3% of patients.
Two-year outcomes of a group of 320 women were also reported at the meeting. Dr. Robert Kuske, of Arizona Breast Cancer Specialists, presented data from the SAVI Collaborative Research Group, which includes 15 U.S. cancer treatment centers using the SAVI applicator.
Treatment was administered at 11 cancer centers and patients received the same breast brachytherapy treatment reported by Yashar. Of the 320 patients, 230 had invasive cancer and 90 had DCIS. Follow-up ranged from 23 months to 59 months. Median age was 63 years, median tumor size was 12 mm, and 87% were postmenopausal.
Grade 2 or greater toxicity at any time post-treatment was low. Kuske reported that seroma formation was weakly associated with a target volume of V90. Telangiectasia development was weakly associated with skin spacing.
Local control was once again excellent, with a recurrence rate of 0.61%. The recurrence rates in both studies were comparable to rates published in peer-review journals for whole-breast irradiation.