Wednesday, November 28 | 3:00 p.m.-3:10 p.m. | SSM01-01 | Arie Crown Theater
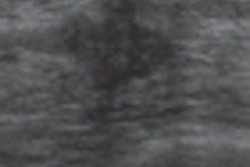
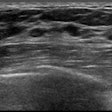
This scientific session will describe how a computer-aided detection (CAD) scheme can help distinguish between benign and malignant masses on breast ultrasound exams.Ultrasound could be useful in breast cancer screening due to its ability, for example, to detect small invasive cancers in dense breasts better than mammography. However, ultrasound also suffers from lower specificity, said presenter Yumi Kashikura of Mie University in Japan.
To see if CAD software could help improve clinician performance, the researchers investigated an internally developed CAD scheme that evaluates the likelihood of histological classifications based on eight objective features.
"Ultrasonographic images have specific features in each histological type, and we thought that it could be useful for clinicians to show the possibility of the histological types," she said.
In an observer study, three experienced clinicians were asked to independently provide subjective ratings on the likelihood of malignancy for each of 390 masses before and after viewing the likelihood of histological classifications provided by the CAD software. Receiver operator characteristics (ROC) analysis showed that CAD yielded a statistically significant increase in the area under the curve.
"It really improved clinicians' performance," Kashikura said.
Kashikura will share more details during her Wednesday talk.