Handheld ultrasound has not yet reached mainstream adoption, but the worldwide market is still projected to reach over $500 million by 2026, according to Signify Research's newly published Handheld Ultrasound Deep Dive Report 2022.
In addition, market revenues are estimated to have grown by approximately 30% in 2021, driven by strong growth in the U.S., the biggest market for handheld ultrasound. Despite the global challenges for handheld ultrasound vendors in 2022, such as rising inflation and supply chain disruptions, the handheld ultrasound market is expected to experience double-digit growth, and this is forecast to continue through to 2026.
Most of the market growth will be fueled by increased adoption of handheld devices by new users of ultrasound, such as primary care physicians, nurses, emergency medical technicians (EMTs), and midwives. The key market trends are discussed below.
AI
The steep learning curve and subsequent ultrasound skills shortage are two of the biggest barriers to the wider use of ultrasound. These challenges are exacerbated in handheld ultrasound, where there is a higher proportion of new and less experienced users compared with cart and compact ultrasound.
As the expansion of the handheld ultrasound market in the coming years is expected to be strongly driven by new user groups, this barrier will be greater than ever before. These barriers can be partially addressed by artificial intelligence (AI) solutions that guide users with positioning and moving the ultrasound probe.
To date, most image guidance AI solutions, such as those from Caption Health, UltraSight, and DESKi, are for cardiac scans. AI image guidance solutions will have a bigger impact when they can also be used for other clinical applications, making it easier for users such as nurses to use ultrasound during their rounds. Though this is starting to happen -- with image guidance AI solutions for the thyroid (developed by Medo.AI), women's health (developed by Pulsenmore), and vascular applications (developed by ThinkSono) -- it will take time, capital, and data to develop image capture support for other body areas. In the interim, we expect to see more anatomy labeling solutions to assist with image capture.
In addition to AI for image capture support, solutions for image analysis will make ultrasound more efficient for users. These applications need to be embraced by physicians, some of whom may be wary about the performance and limitations of AI.
For AI to be more widely used in handheld ultrasound, one of the main challenges that will need to be overcome is how the AI applications are paid for. The solutions need to be affordable to the customer, in line with the price paid for the scanner, yet still enable AI vendors and potential OEM partners to make a profit. Another challenge is validating the AI solutions, which can be costly. This is one of the main reasons for the lack of ultrasound AI adoption in China.
Teleultrasound
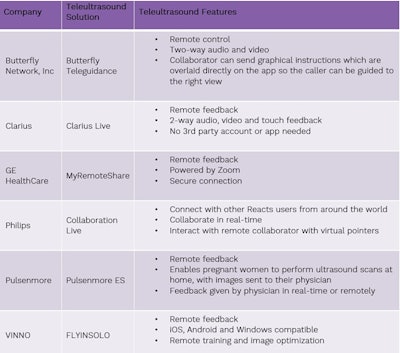
With education being the most significant barrier preventing the adoption of handheld ultrasound, teleultrasound can have a positive influence by connecting novice users with experienced experts. With ultrasound increasingly being taught as part of the curriculum at medical schools, a teleultrasound platform enables newly trained physicians to connect with an ultrasound expert to help them become more comfortable in using ultrasound in real-life cases and to get a second opinion on a diagnosis.
With the current backlog in patients requiring imaging and changes in reimbursement, there is a drive to move imaging to out-of-hospital settings, and teleultrasound platforms, along with other digital solutions, can play a role in facilitating this shift.
Table 1 “Teleultrasound solutions available in the handheld ultrasound market"
Diverging Business Models
During the early years of handheld ultrasound, most devices were purchased with a one-time payment (capital expenditure). This payment model is familiar and accepted by healthcare providers and enables vendors with a broad range of ultrasound systems to sell handheld scanners to their existing customer base as an "add on" with bundled deals.
More recently, the new breed of dedicated handheld ultrasound vendors, like Butterfly Network, Vave, and Clarius Mobile Health, have introduced subscription payment models. Due to the low cost of handheld ultrasound devices, with the global average selling price now down to around $4,000, vendors need large sales volumes to make a profit. This is a challenge as handheld ultrasound has not yet achieved mainstream adoption. As such, most dedicated handheld ultrasound vendors are not yet profitable.
Vendors are now seeking subscription revenue streams, either to replace the upfront payment for the device or to supplement the initial device purchase, to generate additional and recurring revenue. Vendors are now launching digital solutions that are chargeable add-on services, such as teleultrasound and AI applications. Moreover, the subscription model enables vendors to lower the initial cost of the device, opening the market to cost-sensitive customers, such as new users of ultrasound.
Competitive Analysis
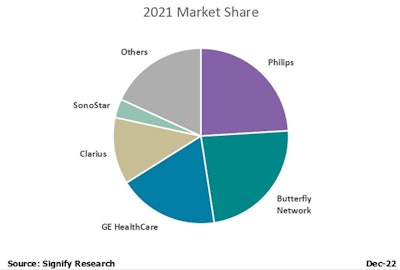
The leading vendors of handheld ultrasound are Philips, Butterfly Network, GE HealthCare, and Clarius. The largest Chinese handheld ultrasound vendors are SonoStar, Youkey, and Stork Healthcare. These vendors are mostly focused on their domestic market, except for SonoStar which has had some limited success in Western Europe and the U.S.
While the market was initially dominated by vendors such as GE HealthCare and Philips with a full ultrasound product portfolio, dedicated handheld vendors are becoming increasingly prominent. Initially competing with other ultrasound system types, notably low-end compact systems, handheld ultrasound vendors are increasingly developing customer bases distinct from users of compact systems. This trend will increase as handheld ultrasound becomes more mainstream and is adopted by increasingly newer users of ultrasound in new use cases such as in plastic surgery and medical aesthetics.
Although the majority of handheld ultrasound sales are wired devices, accounting for around 75% of handheld ultrasound sales revenue in 2021, wireless handheld ultrasound devices are expected to dominate the market in the future. The current product mix of wired versus wireless devices in the market is due more to the supplier mix than customer need, as most vendors currently offer wired devices. Among the larger handheld ultrasound vendors, Butterfly Network and Philips only offer wired devices and GE Healthcare launched its first wireless device in 2021.
The Signify view
The outlook for the handheld ultrasound market is promising, with a projected 2021-2026 compound annual growth rate of 24.7%. Growth will be driven by existing ultrasound users, either to replace compact systems or as an adjunct to existing systems, as well as new users of ultrasound such as nurses, primary care physicians, and midwives. Some vendors are also promoting the use of handheld ultrasound to enable patients to self-scan in the home setting.
Primary care is forecast to be the fastest growing clinical application for handheld ultrasound, with growth propelled by increased adoption of handheld ultrasound by primary care physicians. It is estimated that the percentage of primary care physicians that use ultrasound is in the single digits in most countries. The lower cost and ultraportability of handheld scanners are expected to notably increase the use of ultrasound in primary care.
The use of ultrasound in plastic surgery and medical aesthetics to improve procedure safety, is expected to be one of the fastest emerging applications of handheld ultrasound, especially in Western Europe and the U.S. Ultrasound will increasingly be used by plastic surgeons to differentiate their practice and reassure customers of the safety of cosmetic procedures.
"Handheld Ultrasound Market Deep Dive" presents market dynamics, estimates, forecasts, competitive analysis and major drivers for the handheld ultrasound equipment market. It segments the market into 30 countries/regions and into the five main clinical applications; radiology, cardiology, women's health, point of care, and specialty markets, with these markets subsegmented into 24 clinical applications overall.
Mustafa Hassan is an analyst at Signify Research, an independent supplier of market intelligence and consultancy to the global healthcare technology industry. Signify's major coverage areas are healthcare IT, medical imaging, and digital health.
The comments and observations expressed do not necessarily reflect the opinions of Auntminnie.com or AuntMinnieEurope.com, nor should they be construed as an endorsement or admonishment of any particular vendor, analyst, industry consultant, or consulting group.