Tuesday, November 29 | 9:50 a.m.-10:00 a.m. | MSVB31-07 | Arie Crown Theater
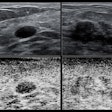
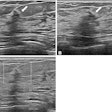
In this Tuesday morning talk, Oslo University Hospital researchers will discuss their study showing that interpretation time for digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) is longer than with full-field digital mammography (FFDM), but it's still acceptable for high-volume batch mode screening.Dr. Per Skaane, PhD, and colleagues compared interpretation times for FFDM and DBT in a population-based mammography screening program, with independent, double reading.
The study included women between ages 50 and 69 attending the screening program; the women were offered two-view DBT in addition to the standard two-view FFDM. The cohort consisted of 4,534 women who had FFDM, 3,356 of these also had DBT. Skaane's group measured interpretation time for all exams from when the case report form was presented to when the reader clicked the mouse to finish.
Skaane's team found that the mean interpretation time for FFDM was 49 seconds (range, 32-81); the mean reading time for DBT was 92 seconds (range, 37-157). Of the 33 cancers detected, 25 had independent double reading for both FFDM and DBT. FFDM missed eight cancers. DBT missed none, for a relative increase in cancer detection of 47%.
Although the reading time for DBT is longer than for FFDM, it could be acceptable even in a high-volume screening program because it finds more cancers than FFDM, Skaane and colleagues concluded.