Using an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm to triage screening mammography exams for interpretation both cuts radiologists' recall rates and their daily reading list, according to a presentation delivered on July 16 at ECR 2022.
The findings could translate to a more efficient screening program by eliminating exams from the to-do list that aren't particularly suspicious, said presenter Dr. Daan Hellingman of Siemens Healthineers in Forchheim, Germany.
"Not reading exams with [lower AI scores -- and thus, less suspicion] can reduce radiologists' recall rates and workload in screening," he said.
Hellingman and colleagues compared an artificial intelligence-based triage strategy for breast cancer screening with independent double radiologist reading with consensus. The AI algorithm scored digital mammography exams for suspicion of cancer on a scale of 1 to 10, with higher scores indicating more suspicion. The study included 37,674 digital mammography exams taken in 2012; of these, 210 cancers were found on screening and 45 were interval cancers.
The AI-based screening algorithm strategy consisted of the following:
- Those exams scored as 9.81 or higher -- the top 1% of most suspicious cases -- were forwarded for recall.
- Those exams with an AI score of 7 to 10 were referred for double reading and a consensus process.
- Those cases with an AI score of 1 to 6 were not referred at all to radiologist readers; these cases made up the majority of the exam pool (73.2%).
Triaging mammography exams using the AI algorithm resulted in a lower recall rate and reduced not only initial reading workload by more than 70% but also consensus reading workload by 45%, Hellingman's group found. The number of cancers identified was equal between the radiologists and the AI algorithm, at 5.6 per 1,000 exams.
| Effect of AI algorithm on mammography exam reading triage | |||
| Measure | No AI triaging | AI triaging | Difference |
| Cancer detection rate | 5.6 per 1,000 exams | 5.6 per 1,000 exams | --- |
| Recall rate | 4.4% | 3.2% | -28% |
| Initial reading workload (exams) | 37,674 | 10,112 | -73% |
| Consensus workload (exams) | 4,255 | 2.336 | -45% |
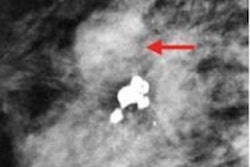
The AI algorithm found five additional cancers among the 1% most suspicious exams, Hellingman noted.
AI shows promise for making breast cancer screening more efficient and effective, but more research is needed.
"The use of AI for decision support has the potential to improve the quality of breast cancer screening ... but prospective studies should confirm this," Hellingman concluded.