Dear Advanced Visualization Insider,
Image segmentation is a requirement for important applications in radiology, such as quantitative imaging, 3D reconstruction, and artificial intelligence (AI)-based cancer detection. In a presentation at last week's Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine (SIIM) meeting, researchers from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, MN, demonstrated how deep-learning algorithms can provide accurate and automated segmentation of the pancreas on CT exams.
In testing, their model performed as well for studies with a normal pancreas as it did for cases with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. You can find out more by reading this edition's Insider Exclusive.
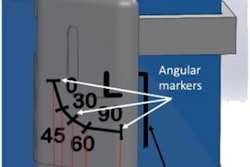
In another talk at SIIM 2021, researchers from the U.S. National Institutes of Health presented their small, 3D-printable device for improving estimates of head-of-bed angle on portable chest x-ray systems. The developers believe the device could help radiologists interpret findings such as pneumonia or other conditions involving pleural effusion.
Advanced visualization topics were also common among presentations at the recent annual International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine meeting. For example, a team from the Medical College of Wisconsin reported that machine-learning models trained using autopsy tissue samples were able to reveal new information on brain tumor pathology from MRI exams.
Also, South Korean researchers shared how machine-learning algorithms developed using radiomics and clinical imaging findings were able to accurately detect cancer on breast MRI. Another talk focused on how cloud computing can support a number of imaging applications, including real-time image reconstruction, automated quantitative perfusion mapping in MRI cardiovascular stress testing, and training of AI algorithms.
In other developments, investigators from Oregon Health and Science University described how augmented reality technologies could soon deliver a breakthrough in image-guided surgical procedure planning and navigation. And a new MRI technique called 3D amplified MRI was able to visualize brain disorders in real-time in two recent studies. A multi-institutional group of researchers believes the method could potentially reveal hidden brain conditions before they become life-threatening.
3D-printed shields produced from CT scans can be used to protect healthy structures in the gastrointestinal tract during radiation procedures. And image-reconstruction software based on deep-learning algorithms yielded more accurate measurements of pulmonary nodules on low-dose chest CT exams than conventional reconstruction techniques.
Is there a story you'd like to see covered in the Advanced Visualization Community? Please feel free to drop me a line.