J Nucl Med 2002 Nov;43(11):1419-25
Automated detection of local normalization areas for ictal-interictal
subtraction brain SPECT.
Boussion N, Houzard C, Ostrowsky K, Ryvlin P, Mauguiere F, Cinotti L.
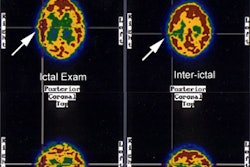
Whole-brain activity is often chosen to quantitatively normalize peri-ictal and
interictal SPECT scans before their subtraction. This use is not justified,
because significant and extended modification of the cerebral blood flow can
occur during a seizure. We validated and compared 2 automatic methods able to
determine the optimal reference region, using simulation and clinical data.
METHODS: In the first method, the selected reference region is the intersection
of peri-ictal-interictal areas with no significantly different z values. The
other method relies on a 3-dimensional iterative voxel aggregation. The increase
of the selected volume is stopped by using 2 different variance tests (Levene
and SE). These algorithms were tested on 39 epileptic patients and were
validated using 1 interictal and 10 peri-ictal scans simulated from the mean
image of 22 healthy subjects. RESULTS: In the patient studies, the mean relative
activity of the selected regions, compared with whole-brain activity (classic
normalization), was 122.6%. Their average relative size (compared with the size
of the whole brain) was 33.2% for the z map method, 22.8% for the SE test, and
11.8% for the Levene test. After application of our automatic processes,
subtraction of the simulated images revealed a recovery of abnormal regions up
to 45% larger than the region obtained with classic normalization. CONCLUSION:
These results illustrate the role of normalization on the subtracted peri-ictal
and interictal images. Our methods are automatic and objective and give good
results on various simulated images. The z map construction is worth considering
because it is simple, selects large parts of the brain, and requires little
computation time.