AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999 Apr;172(4):1027-31
Direct versus indirect signs of traumatic aortic injury revealed by
helical CT: performance characteristics and interobserver agreement.
Fishman JE, Nunez D Jr, Kane A, Rivas LA, Jacobs WE.
OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relative value of and
interobserver agreement on direct versus indirect (hematoma) signs of traumatic aortic
injury using helical CT. MATERIALS AND METHODS: From April 1994 through January 1997, 40
patients who were suspected to have traumatic aortic injury and who underwent
contrast-enhanced helical CT had subsequent proof or exclusion of aortic injury. All
available CT scans of these patients were combined with CT scans of 13 randomly chosen
patients that had been initially interpreted as negative, and clinical follow-up showed no
evidence of aortic injury. Two emergency radiologists and a nonemergency radiologist who
were unaware of clinical outcome performed independent review of these cases to evaluate
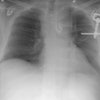
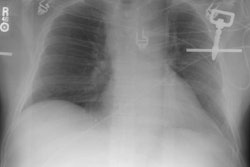
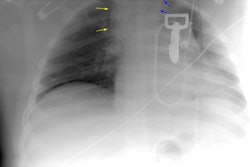
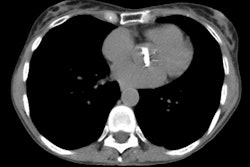
for mediastinal hematoma, periaortic hematoma, and direct signs of aortic injury. RESULTS:
Direct signs of injury were seen on helical CT by both emergency radiologists in all 17
cases of aortic injury with no false-positive interpretations. The nonemergency
radiologist failed to observe subtle direct signs in two cases of aortic injury, but
patient management would not have been adversely affected. All observers had more
false-negative interpretations for both mediastinal hematoma and periaortic hematoma than
for direct signs. Interobserver agreement was higher for direct signs (kappa = .93) than
for either mediastinal hematoma (kappa = .65) or periaortic hematoma (kappa = .71).
CONCLUSION: In this study, helical CT revealed direct signs of traumatic aortic injury
that were more accurate and more often observed than were indirect signs. Emphasis on
direct signs should improve confidence in using helical CT to evaluate traumatic aortic
injury.