NEW YORK (Reuters Health), Mar 26 - A functional polymorphism in the gene that encodes growth differentiation factor 5 (GDF5) increases the susceptibility to osteoarthritis (OA), according to a report in the March 25th advance online publication of Nature Genetics.
"This gives us a starting point to uncover the molecular mechanism of OA, which will result in the development of better treatment," Dr. Shiro Ikegawa from SNP Research Center, Tokyo, Japan told Reuters Health.
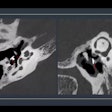
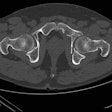
Dr. Ikegawa and associates sequenced genomic DNA from 24 individuals with hip osteoarthritis to identify single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in GDF5 and compared the genotypic and allelic frequencies of three identified SNPs in 239 individuals with hip osteoarthritis and 256 controls.
The most significant association with hip OA was seen in a SNP in the 5' untranslated region of GDF5 (rs143383, +104T/C), the authors report. The presence of +104T independently increased the risk of hip OA by 79%.
The presence of +104T was also associated with a 30% increase in the risk for knee OA in the Japanese population and a 54% increase in the risk for knee OA in a Han Chinese population, the results indicate.
This allele showed significantly lower promoter activity, resulting in significantly less transcription in two chondrogenic cell lines, the researchers note.
"Each of these findings points to an important role for GDF5 in articular cartilage homeostasis and indicates that decreased GDF5 expression may lead to susceptibility for osteoarthritis," the investigators conclude. "Therefore, increased GDF5 expression or enhancement of its downstream signal could help to prevent osteoarthritis."
By Will Boggs, MD
Last Updated: 2007-03-26 10:02:37 -0400 (Reuters Health)
Nature Genetics 2007.
Related Reading
Stem cells from osteoarthritis patients used to engineer cartilage tissue, February 2, 2007
Copyright © 2007 Reuters Limited. All rights reserved. Republication or redistribution of Reuters content, including by framing or similar means, is expressly prohibited without the prior written consent of Reuters. Reuters shall not be liable for any errors or delays in the content, or for any actions taken in reliance thereon. Reuters and the Reuters sphere logo are registered trademarks and trademarks of the Reuters group of companies around the world.