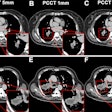
Virtual colonoscopy providers have long envisioned a future without cathartic bowel cleansing. In a newly published study, researchers from Belgium experimented with a completely laxative-free regimen consisting of fecal tagging and a low-residue diet, with promising results.
"Laxative-based preparations are a major burden for the patients, interrupting normal daily activities because of possible fulminant diarrhea and side effects such as abdominal discomfort, nausea, and vomiting," the researchers wrote in a paper published in the American Journal of Roentgenology. "Fecal tagging has been used successfully in combination with full and reduced cathartic cleansing. Besides an improved differentiation between stool and polyps, the method permits more residue to be left in the colon, and hence a reduction of the cathartic part of the preparation," (October 2004, Vol. 183:4, pp. 945-954).
The researchers sought to develop an efficient method of performing virtual colonoscopy using fecal tagging and a low-residue diet, but no purgative cleansing regimen. To this end, 15 patients (four men, 11 women, ages 23-73) who were referred for colonoscopy (for vague abdominal pain or other indications) also agreed to undergo the laxative-free VC exam. None of them complained of constipation or irritable bowel syndrome.
The day before virtual colonoscopy, the patients began to eat a dedicated low-residue diet (NutraPrep, E-Z-EM, Lake Success, NY) combined with hydration control, which limited their fluid intake to 2 L per day. The diet, consisting of low-residue foods such as potato chips and apple sauce, was aimed at reducing fecal output and controlling fat intake, the authors wrote.
In an effort to determine the best barium concentration, fecal tagging was performed with five different barium suspensions in three patients each, including 2.1%, 4%, and 40% barium by weight/volume (w/v) (Tagitol, E-Z-EM).
Group 1 ingested a total of 750 mL of a 2.1 w/v suspension barium the day before VC, and 250 mL of barium at three meals per day (total 15.75 g of barium). Group 2 had the same protocol, except that their morning-meal barium concentration was 4% (total 10.5 g of barium). Group 3 ingested barium over two days, using a 4% suspension the first day and 2.1% suspension the second day (total 21.75 g of barium). Group 4 ingested a 40% w/v barium suspension a day before the exam (total 20 g of barium). Finally, group 5 ingested a 40% barium suspension over two days, 12.5 mL with each meal the first day and 25 mL with each meal the second day (total 25 g of barium), according to the authors.
Virtual colonoscopy was performed following the administration of hyoscine-N-butylbromide (Buscopan, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ingelheim, Germany) and inflation of the colon with room air. A single-slice Tomoscan AV/EU scanner (Philips Medical Solutions, Andover, MA) was used to acquire the images at 5-mm collimation, 7-mm table feed, pitch 1.4, and 3-mm reconstruction interval. The scans were reviewed on an innerviewGI workstation (E-Z-EM).
Using a protocol previously described by Callstrom et al, the efficacy of fecal tagging was assessed by electronically labeling all residue with a density exceeding 150 HU, and visually evaluated on the axial scans.
Scores of 0% (untagged), 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% (completely tagged) were used to evaluate each colon segment, and average scores per segment and per patient were calculated. Fluid was also assessed according to the proportion of lumen it occupied.
According to the results, the subjective fecal labeling scores varied between 90% and 100% for all patients, "except for the descending colon in group 2, in which a score of only 71% was obtained," owing to one patient having a small untagged stool that did not impede examination of the colonic wall, the authors explained.
"No difference in labeling was seen between patients who ingested barium over the course of one versus two days, and between patients who received the 750-mL barium dose and those receiving the 50-mL barium dose the day before CT colonography," they wrote. "In all patients of all groups, a 100% labeling score was obtained in the cecum."
Moreover, the hydration control (2 L per day) left most patients in the cohort with a dry colon, except in one patient. The fluid quantities would need to be increased in warmer climates, they stated. As for barium tagging, the authors concluded that "efficient and homogeneous tagging" was confirmed by the results of the electronic labeling.
"No difference of efficacy in labeling the fecal residue was noted between the patients who ingested barium for one day and those who ingested barium over the course of two days," the authors wrote. However, the method could be less efficient in patients, especially older patients, who do not have a normal stool habit because of irritable bowel syndrome, constipation, or diverticulosis. Such patients might require more barium."
Other limitations include the small patient cohort. The results need to be confirmed in a large, polyp-rich group, they stated.
The ability to perform virtual colonoscopy without cathartic cleansing regimen would dramatically improve patient compliance, the authors wrote, adding that reducing the fluid-intake restrictions in the present protocol would also improve compliance.
A dedicated low-residue diet in combination with barium fecal tagging and hydration control without cathartic bowel cleansing "produced an almost completely dry colon with efficient tagging of fecal residue," the group concluded.
By Eric Barnes
AuntMinnie.com staff writer
November 10, 2004
Related Reading
VC antispasmodics show mixed distension results, real patient-acceptance gains, August 27, 2004
Reduced-prep VC with tagging works after failed colonoscopy, March 7, 2004
German group optimizes barium-sulfate tagging in MR colonography, January 22, 2003
In virtual colonoscopy, nothing beats a good prep, July 16, 2002
Fecal tagging improves detection in virtual colonoscopy, August 29, 2002
Copyright © 2004 AuntMinnie.com