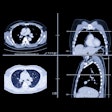
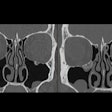
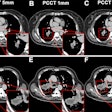
A new study from the University Hospital Zurich in Switzerland has found that dual-source CT achieves a lower effective radiation dosage for a heart examination than conventional CT.
The study also demonstrated that stenoses can be diagnosed with similar high accuracy as invasive x-ray angiography. The results of the study were published in the June issue of Heart, the official journal of the British Cardiovascular Society.
Researchers analyzed 120 patients with suspected coronary heart disease who were scanned with Erlangen, Germany-based Siemens Healthcare's Somatom Definition CT scanner, which features two x-ray tubes. Siemens' Adaptive Cardio sequence with a step-and-shoot mode was used with the dual-source CT to reduce radiation dose.
The results show that CT coronary angiography with a dual-source CT in step-and-shoot mode produces images of excellent diagnostic quality in patients with stable heart rates up to 70 beats per minute, the researchers said. The study required an effective dose of 2.5 mSv on average with a deviation of plus/minus 0.8 mSv. In previous research, a normal average effective dose for heart scans was between 9 mSv and 21 mSv.
Related Reading
Acuson P10 used in remote Kilimanjaro, July 9, 2008
Siemens to cut 16,700 jobs, 2,800 in healthcare, July 8, 2008
Siemens inks 3T R&D partnership, July 3, 2008
Siemens places first S2000 scanner in U.K., July 2, 2008
Siemens signs York Hospital, June 26, 2008
Copyright © 2008 AuntMinnie.com